Introduction
Have you ever wondered how water makes its way effortlessly from a lower to a higher place, especially in industrial settings or your home garden fountain? Enter the centrifugal pump, an unsung hero in the world of hardware tools. This ingenious device not only exemplifies the beauty of physics in action but also serves as a reliable companion for countless applications. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of centrifugal pumps and explore why they deserve a spot in the limelight.
The Basics of Centrifugal Pumps
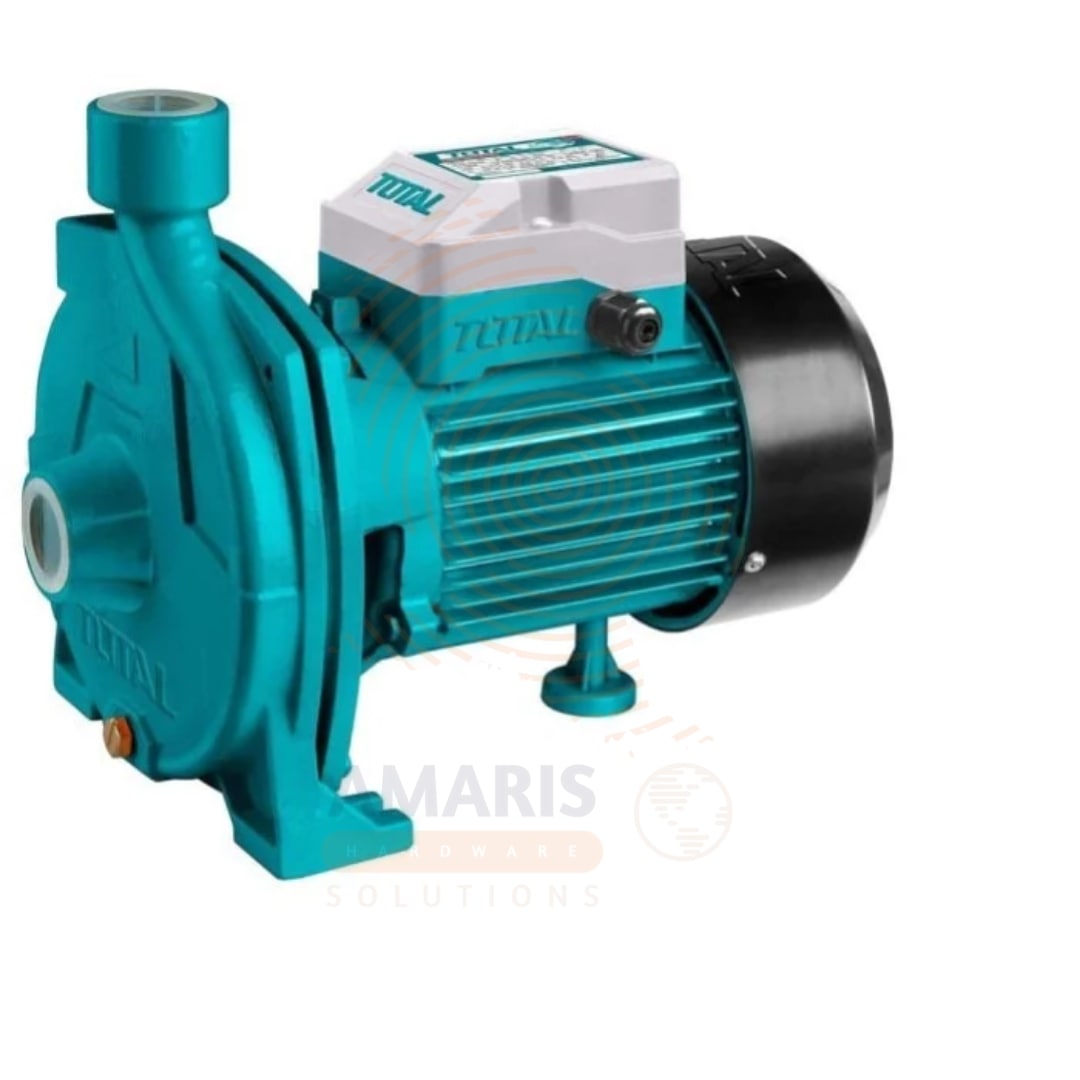
At its core, a centrifugal pump is a mechanical device designed to move fluids by converting rotational kinetic energy to hydrodynamic energy. Imagine a merry-go-round: as it spins, anything on it moves outward. Similarly, a centrifugal pump uses a spinning impeller to push water (or any fluid) from the center of the pump outwards to its edges, creating flow and pressure.
Key Components
- Impeller: The heart of the pump. It’s a rotating disk with vanes that accelerates the fluid outward.
- Volute: The casing that catches the fluid from the impeller and directs it to the discharge point.
- Shaft: Connects the impeller to the motor, transmitting the rotational energy.
- Motor: The power source, often electric, that drives the impeller.
How It Works
When the pump is activated, the motor spins the impeller. As the impeller rotates, it imparts kinetic energy to the fluid. Due to centrifugal force, the fluid is flung outward from the impeller’s center to its edges, where it gains velocity. The volute then collects this high-velocity fluid and gradually converts its kinetic energy into pressure energy as it exits the pump.
Imagine the impeller as a spinning dancer on a stage. As the dancer twirls faster, her skirt flares outwards, similar to how the fluid moves within the pump. This dynamic motion is what propels the fluid forward, overcoming gravity and resistance.
Applications Galore
Centrifugal pumps are ubiquitous and versatile, finding applications in various fields:
- Water Supply Systems: Ensuring homes and buildings have a steady water supply.
- Agriculture: Irrigating fields and supplying water to livestock.
- Chemical Industry: Handling aggressive chemicals and ensuring safe fluid transport.
- Oil and Gas: Moving oil through pipelines and aiding in refinery processes.
- HVAC Systems: Circulating coolant and maintaining temperature control in large buildings.
Why Centrifugal Pumps are Awesome
- Simplicity: With fewer moving parts, these pumps are easier to maintain and repair.
- Efficiency: They can handle large volumes of fluid with minimal energy consumption.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of fluids, from water to chemicals.
- Reliability: Built to withstand tough conditions and deliver consistent performance.
Fun Facts
- Ancient Roots: The concept of using centrifugal force to move fluids dates back to the ancient Persian windmill.
- High-Speed Action: Some centrifugal pumps can spin at speeds of up to 30,000 RPM, faster than a Formula 1 car engine!
- Mini Marvels: Micro centrifugal pumps, no larger than a coin, are used in medical devices for precise fluid control.
Conclusion
Centrifugal pumps might not be the flashiest tool in your hardware arsenal, but their role is undeniably crucial. These marvels of engineering effortlessly harness the power of centrifugal force to move fluids, making our lives easier in countless ways. The next time you see water gushing out of a fountain or flowing through irrigation channels, take a moment to appreciate the centrifugal pump working tirelessly behind the scenes. It’s a true testament to human ingenuity and the wonders of physics!

















Add comment