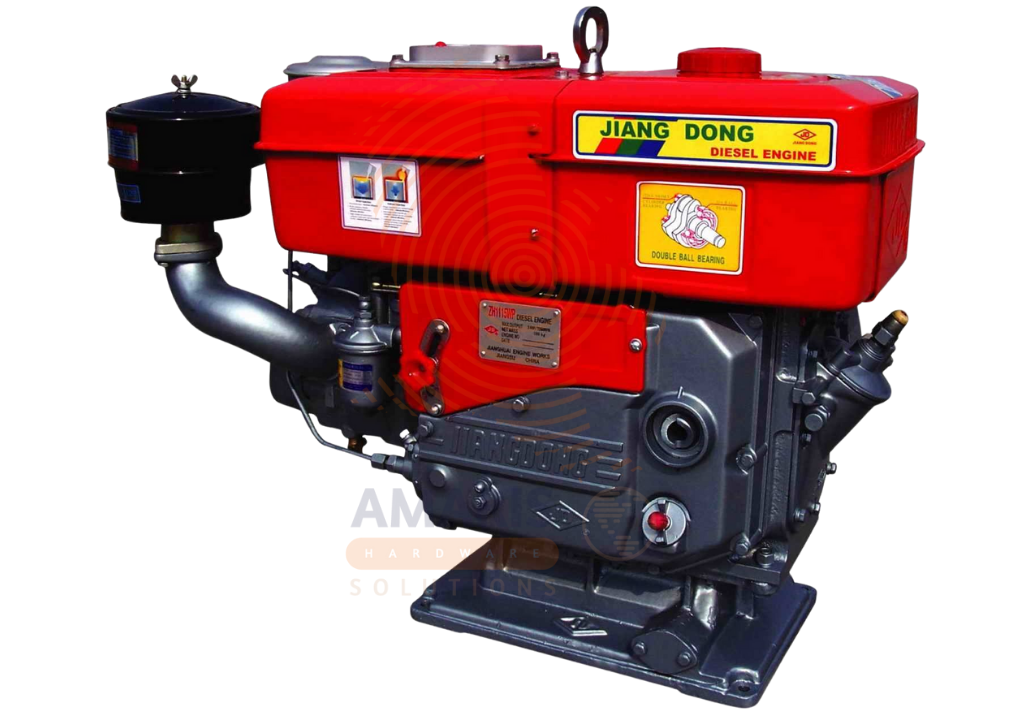

Diesel Engine
$242.31 Original price was: $242.31.$230.19Current price is: $230.19.
A diesel engine is a type of internal combustion engine that operates by compressing air to a high temperature and then injecting diesel fuel into the combustion chamber, where it ignites spontaneously. Known for its fuel efficiency, durability, and high torque output, diesel engines are widely used in automotive, industrial, agricultural, and construction applications. These engines can range from small single-cylinder types to large multi-cylinder units used in heavy-duty machinery and generators. Unlike gasoline engines, diesel engines do not require spark plugs, making them more robust and suitable for continuous and heavy workloads in demanding environments.
Table of Contents
ToggleDiesel Engine
Uses
-
Construction Machinery
-
Powers equipment such as excavators, bulldozers, backhoes, compactors, and cranes.
-
Provides reliable energy for machines operating in remote or rugged job sites.
-
-
Agricultural Equipment
-
Used in tractors, harvesters, irrigation pumps, sprayers, and plows.
-
Offers high torque for pulling heavy loads and operating farm implements.
-
-
Industrial Applications
-
Powers compressors, conveyors, crushers, generators, and drilling rigs.
-
Integral to industries like mining, quarrying, and material processing.
-
-
Generators and Power Backup
-
Used in diesel generators for backup and continuous power supply in homes, hospitals, factories, and construction sites.
-
Ideal for off-grid or emergency applications due to fuel efficiency and reliability.
-
-
Water Pumps and Irrigation Systems
-
Drives diesel-powered water pumps for agricultural, municipal, and construction water management.
-
Suitable for regions with inconsistent electric supply.
-
-
Transport and Vehicles
-
Common in trucks, buses, ships, trains, and off-road vehicles due to better mileage and durability.
-
Used in fleets requiring high-load hauling and long service life.
-
-
Marine Applications
-
Powers boats, barges, and ships, offering long runtime, reliability, and low maintenance.
-
Used in both propulsion and onboard systems (like pumps and generators).
-
-
Heavy Equipment & Earthmoving
-
Essential for graders, rollers, wheel loaders, and other ground preparation equipment.
-
Provides consistent power under heavy mechanical loads.
-
-
Mobile Lighting and Air Compressors
-
Powers portable lighting towers and high-capacity air compressors used on construction and mining sites.
-
-
Military and Emergency Equipment
-
Used in military transport vehicles, field power units, and emergency response equipment due to reliability in extreme conditions.
Safety Precautions
-
Wear Protective Gear
-
Use safety glasses or goggles to protect eyes from fuel spray or debris.
-
Wear gloves when handling diesel or engine components.
-
Use hearing protection if operating in high-noise environments.
-
Wear flame-resistant clothing when working near hot or combustible engine parts.
-
-
Fire and Fuel Safety
-
Store diesel fuel in approved, labeled containers and away from ignition sources.
-
Do not refuel while the engine is running or hot.
-
Keep a fire extinguisher (Class B) nearby in case of spills or fires.
-
-
Proper Ventilation
-
Operate diesel engines only in well-ventilated areas to avoid inhaling exhaust gases.
-
Use exhaust extension systems or ducts in enclosed workspaces.
-
-
Prevent Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
-
Never run diesel engines in confined spaces without proper air circulation.
-
Install carbon monoxide detectors in indoor or semi-enclosed operation areas.
-
-
Routine Inspection
-
Check for fuel leaks, cracked hoses, damaged wiring, or loose connections before operation.
-
Inspect oil levels, coolant levels, air filters, and belts regularly.
-
-
Hot Surface Awareness
-
Avoid contact with hot engine parts such as the exhaust manifold, cylinder head, and turbocharger.
-
Allow engine to cool before performing maintenance or refueling.
-
-
Safe Starting Procedure
-
Ensure all safety guards are in place before starting.
-
Use the correct starting sequence (e.g., glow plugs if equipped).
-
Do not attempt to start the engine by bypassing safety systems.
-
-
Handling Exhaust Systems
-
Avoid standing directly in the exhaust stream.
-
Use mufflers or filters to control emissions in sensitive environments.
-
-
Electrical Safety
-
Disconnect battery terminals before conducting electrical repairs.
-
Ensure battery is securely mounted and cables are insulated.
-
-
Training and Compliance
-
Only trained personnel should operate or service diesel engines.
-
Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule and safety guidelines.
-
Stay updated on environmental regulations related to diesel emissions.


 Acrylic Sealants
Acrylic Sealants Construction Adhesives
Construction Adhesives Double-Sided Tape
Double-Sided Tape Duct Tape
Duct Tape Electrical Tape
Electrical Tape Epoxy & Resins
Epoxy & Resins Masking Tape
Masking Tape
 Automotive Wrenches & Socket Sets
Automotive Wrenches & Socket Sets Battery Chargers & Jump Starters
Battery Chargers & Jump Starters Car Jacks & Stands
Car Jacks & Stands Car Wash & Detailing Products
Car Wash & Detailing Products Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic Tools Tire Inflators
Tire Inflators Vehicle Lighting
Vehicle Lighting Oil & Lubricants
Oil & Lubricants
 Adhesives & Sealants
Adhesives & Sealants Bricks & Blocks
Bricks & Blocks Cement & Concrete
Cement & Concrete Drywall & Plaster
Drywall & Plaster Flooring (Tiles, Wood, Laminate)
Flooring (Tiles, Wood, Laminate) Lumber & Plywood
Lumber & Plywood Paints, Primers & Coatings
Paints, Primers & Coatings Insulation Materials
Insulation Materials Roofing Materials
Roofing Materials
 Circuit Breakers
Circuit Breakers Electrical Cables & Wires
Electrical Cables & Wires Switches & Sockets
Switches & Sockets Fuses & Relays
Fuses & Relays Connectors & Terminals
Connectors & Terminals Electrical Boxes & Panels
Electrical Boxes & Panels Conduit & Fittings
Conduit & Fittings Lighting Fixtures & Bulbs
Lighting Fixtures & Bulbs Extension Cords & Power Strips
Extension Cords & Power Strips
 Anchors
Anchors Bolts
Bolts Clips & Clamps
Clips & Clamps Screws
Screws Nuts
Nuts Washers
Washers Rivets
Rivets Nails
Nails Threaded Rods
Threaded Rods
 Hammers
Hammers Measuring Tools (Tapes, Levels, Calipers)
Measuring Tools (Tapes, Levels, Calipers) Screwdrivers
Screwdrivers Pliers & Cutters
Pliers & Cutters Saws & Blades
Saws & Blades Chisels & Punches
Chisels & Punches Allen Keys & Hex Keys
Allen Keys & Hex Keys Ratchets & Socket Sets
Ratchets & Socket Sets Wrenches & Spanners
Wrenches & Spanners
 Power Tool Accessories (Blades, Bits, Discs)
Power Tool Accessories (Blades, Bits, Discs) Rotary Tools
Rotary Tools Saws (Circular, Jigsaw, Reciprocating)
Saws (Circular, Jigsaw, Reciprocating) Drills & Drivers
Drills & Drivers Grinders & Sanders
Grinders & Sanders Heat Guns
Heat Guns Nail Guns
Nail Guns Impact Wrenches
Impact Wrenches Batteries & Chargers
Batteries & Chargers
 Pipes & Fittings (PVC, Copper, PEX)
Pipes & Fittings (PVC, Copper, PEX) Plumbing Tools
Plumbing Tools Pumps & Motors
Pumps & Motors Sealants & Adhesives for Plumbing
Sealants & Adhesives for Plumbing Valves & Taps
Valves & Taps Water Heaters
Water Heaters Drainage Systems
Drainage Systems Faucets & Fixtures
Faucets & Fixtures Hoses & Tubing
Hoses & Tubing
 Hinges & Latches
Hinges & Latches Hooks & Brackets
Hooks & Brackets Window Hardware
Window Hardware Chains & Cables
Chains & Cables Casters & Wheels
Casters & Wheels Shelving & Storage Systems
Shelving & Storage Systems Door Handles & Locks
Door Handles & Locks Drawer Slides & Cabinet Hardware
Drawer Slides & Cabinet Hardware
 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Respirators & Masks
Respirators & Masks Safety Glasses
Safety Glasses Safes
Safes Security Cameras
Security Cameras Gloves
Gloves Helmets
Helmets Ear Protection
Ear Protection Fire Safety Equipment
Fire Safety Equipment Locks & Padlocks
Locks & Padlocks Motion Sensors & Alarms
Motion Sensors & Alarms
 Garden Fencing
Garden Fencing Garden Furniture Hardware
Garden Furniture Hardware Lawn Mowers
Lawn Mowers Trimmers & Edgers
Trimmers & Edgers Shovels & Spades
Shovels & Spades Rakes & Hoes
Rakes & Hoes Pruning Shears & Loppers
Pruning Shears & Loppers Watering Systems (Hoses, Sprinklers, Nozzles)
Watering Systems (Hoses, Sprinklers, Nozzles)
 Interior Paints
Interior Paints Paint Brushes & Rollers
Paint Brushes & Rollers Paint Strippers & Thinners
Paint Strippers & Thinners Paint Trays & Accessories
Paint Trays & Accessories Exterior Paints
Exterior Paints Spray Paints
Spray Paints Primers & Undercoats
Primers & Undercoats Varnishes & Stains
Varnishes & Stains
 Gaskets & Seals
Gaskets & Seals Hydraulic Fittings
Hydraulic Fittings Industrial Fasteners
Industrial Fasteners Industrial Hoses
Industrial Hoses Lubricants & Greases
Lubricants & Greases Metal Sheets & Bars
Metal Sheets & Bars Bearings & Bushings
Bearings & Bushings Belts & Pulleys
Belts & Pulleys
 HVAC Filters
HVAC Filters Insulation for HVAC
Insulation for HVAC Air Conditioners
Air Conditioners Refrigerants
Refrigerants Ventilation Ducts & Fittings
Ventilation Ducts & Fittings Thermostats & Controllers
Thermostats & Controllers Fans & Blowers
Fans & Blowers
 Pegboards & Hooks
Pegboards & Hooks Shelving Units
Shelving Units Storage Bins & Containers
Storage Bins & Containers Toolboxes & Tool Chests
Toolboxes & Tool Chests Workbenches
Workbenches Drawer Organizers
Drawer Organizers Labeling Supplies
Labeling Supplies
 Welding Accessories (Clamps, Brushes)
Welding Accessories (Clamps, Brushes) Welding Electrodes & Rods
Welding Electrodes & Rods Welding Helmets & Gloves
Welding Helmets & Gloves Welding Machines
Welding Machines Soldering Irons & Stations
Soldering Irons & Stations Flux & Solder Wire
Flux & Solder Wire
 Generator Accessories
Generator Accessories Inverters
Inverters Portable Generators
Portable Generators Power Inverters
Power Inverters Transfer Switches
Transfer Switches Diesel & Gasoline Generators
Diesel & Gasoline Generators
 Transport Equipment: Carts, Dollies, and Hand Trucks
Transport Equipment: Carts, Dollies, and Hand Trucks Storage Solutions: Pallets, Racks, and Containers
Storage Solutions: Pallets, Racks, and Containers Lifting Equipment: Hoists, Cranes, and Jacks
Lifting Equipment: Hoists, Cranes, and Jacks Conveyors & Accessories: Belts & Rollers
Conveyors & Accessories: Belts & Rollers
 Office Chairs
Office Chairs











