Basin Wrench with Fixable Head
$ 17.31 Original price was: $ 17.31.$ 16.44Current price is: $ 16.44.

Battery Clamps Set
$ 13.46 Original price was: $ 13.46.$ 12.79Current price is: $ 12.79.
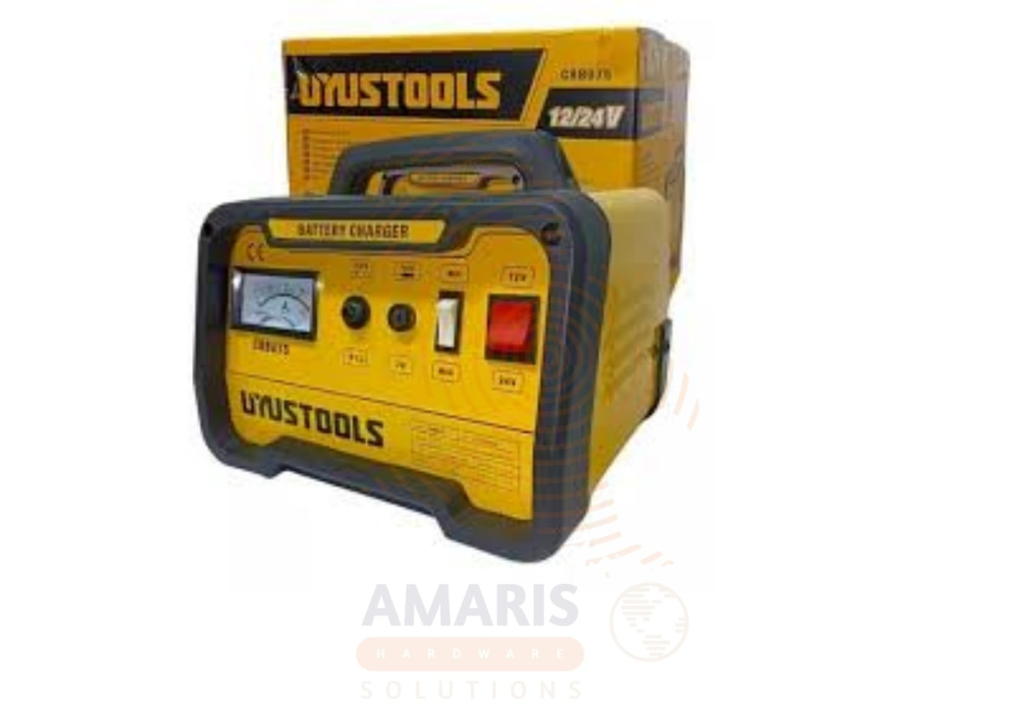
12 And 24V Battery Charger
$ 75.00 Original price was: $ 75.00.$ 71.25Current price is: $ 71.25.
WhatsApp Order
A 12 And 24V Battery Charger is a device designed to replenish the energy in rechargeable batteries with voltage specifications of 12 volts or 24 volts. These chargers typically employ electrical currents to restore the energy levels of batteries, allowing them to be reused. The dual voltage capability indicates that the charger is versatile enough to accommodate both 12-volt and 24-volt battery systems, making it suitable for a variety of applications, such as automotive, marine, or industrial use. The charging process involves delivering a controlled flow of electrical power to the battery, ensuring a safe and efficient recharging cycle.
Categories: AUTOMOTIVE TOOLS & ACCESSORIES, Batteries & Chargers, Battery Chargers & Jump Starters, POWER TOOLS
Tags: automotive battery charger, battery charger, durable charger, electric charger, fast charging, portable charger, power tool charger, rechargeable battery charger, tool battery charger
Description
Table of Contents
Toggle12 And 24V Battery Charger
Uses
-
Automotive Maintenance:
-
Charging car batteries: 12V chargers are commonly used for charging the batteries in cars, motorcycles, and other automotive vehicles.
-
Charging commercial vehicle batteries: Some larger vehicles, like trucks and buses, may have 24V battery systems.
-
-
Marine Applications:
-
Boats and yachts often use 12V or 24V battery systems for various functions, such as starting engines, powering navigation equipment, and lighting.
-
-
RVs and Campers:
-
Many recreational vehicles and camper trailers use 12V or 24V battery systems for auxiliary power, lighting, and appliances.
-
-
Industrial Equipment:
-
Forklifts, industrial machinery, and other equipment in manufacturing settings may use 12V or 24V batteries, and chargers are essential for maintaining their operational readiness.
-
-
Solar Power Systems:
-
Off-grid solar power systems often use batteries to store energy for later use, and 12V or 24V battery chargers can be employed to recharge these batteries when needed.
-
-
Emergency Power Supplies:
-
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems that provide backup power for critical equipment often use 12V or 24V batteries, and chargers play a role in keeping these batteries charged and ready.
-
-
Recreational Vehicles and Equipment:
-
ATVs, snowmobiles, and other recreational vehicles may use 12V or 24V batteries, and chargers are essential for maintaining their power supply.
-
-
Remote Power Stations:
-
Remote communication stations, weather stations, and other off-grid installations often rely on batteries for power, and 12V or 24V chargers can be used to keep these batteries charged.
-
-
Electric Scooters and Bicycles:
-
Some electric scooters and bicycles use 12V or 24V battery systems, and chargers are necessary for recharging these batteries.
-
-
Emergency Backup Systems:
-
Emergency backup systems, such as those used in hospitals or data centers, may incorporate 12V or 24V batteries, and chargers are crucial for ensuring these systems are always ready in case of a power outage.
-
SAFETY HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
Safety Precautions
-
Read the User Manual:
· Familiarize yourself with the user manual provided by the manufacturer. It contains critical information about compatible battery types, charging procedures, indicator lights, and specific safety guidelines. -
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
· Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from potential battery leakage or sparks. Consider wearing gloves when handling old or damaged batteries. -
Inspect the Charger and Battery:
· Before use, inspect the battery charger for any damage to the cord, plug, or casing. Examine batteries for cracks, leaks, corrosion, or swelling. Do not use damaged components. -
Use the Correct Charger for the Battery:
· Use only the charger designed for the specific battery chemistry (e.g., Li-ion, NiMH, Lead-Acid), voltage, and capacity. Using an incompatible charger can cause fire, explosion, or battery damage. -
Set Up in a Safe Location:
· Place the charger and battery on a stable, non-flammable, dry, and well-ventilated surface. Keep away from heat sources, flammable materials, moisture, and direct sunlight. -
Disconnect Power When Not in Use:
· Unplug the charger from the wall outlet when it is not actively charging batteries. This prevents potential electrical hazards and saves energy. -
Maintain a Clear and Dry Work Area:
· Keep your charging area clean, dry, and organized. Ensure the charger vents are not blocked to prevent overheating. -
Proper Connection Technique:
· Connect the battery to the charger securely, ensuring correct polarity (positive/+ to positive, negative/- to negative). Connect the charger to the power outlet last. -
Never Leave Charging Unattended for Extended Periods:
· Do not leave batteries charging unattended for long periods (e.g., overnight or while away from home) unless the charger is specifically designed for maintenance or float charging and you have followed manufacturer guidelines. -
Dispose of Waste Properly:
· Dispose of old, leaking, or damaged batteries at a designated recycling or hazardous waste facility. Do not dispose of in regular household trash. -
Keep Objects Away:
· Ensure metal objects like tools, keys, or jewelry do not come into contact with the battery terminals to prevent short circuits, which can cause fire or burns. -
Store the Tool Safely:
· After use, unplug the charger and store it in a cool, dry place away from children and pets. Store batteries separately in a non-conductive container, protected from short-circuiting.
Related products
Bi-Metal Hole Saw Set
A Bi-Metal Hole Saw Set refers to a collection of nine hole saws, each constructed with a bi-metal design. A hole saw is a cylindrical cutting tool used to create holes in various materials such as wood, metal, plastic, and more. The term "bi-metal" indicates that the hole saws are made from two different types of metals, typically high-speed steel (HSS) and a more durable alloy like cobalt. This combination enhances the hole saw's cutting performance, making it suitable for a wide range of applications and providing increased durability and longevity. The set typically includes hole saws of different sizes to accommodate various hole diameters, making it a versatile tool for professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike.
Chain Saw Adapter for Angle Grinder
Chain Saw Adapter for Angle Grinder typically refer to components that allow you to attach or use certain accessories with your chainsaw or grinder.
- Chainsaw Adapter:
- A device that enables the use of a 12-inch chainsaw blade on a chainsaw designed for a different blade size. This adapter allows you to customize or replace the original chainsaw blade with a 12-inch one, potentially for different cutting applications.
- Grinder Adapter:
- An accessory that allows you to attach a grinder to a 12-inch chainsaw, converting it into a chainsaw chain sharpener. This adapter facilitates the grinding or sharpening of the chainsaw chain, ensuring optimal cutting performance.
Chuck Die Grinder
A Chuck Die Grinder is a handheld power tool equipped with a collet or chuck that holds a rotary burr or abrasive head. This tool is commonly used for precision grinding, polishing, and shaping of metal, wood, plastic, and other materials. Chuck Die Grinders are versatile and compact, allowing for intricate and detailed work in various applications, including metalworking, woodworking, and fabrication. They are widely employed in industries such as machining, automotive, and aerospace, as well as by hobbyists and craftsmen for tasks requiring fine control and high-speed material removal.
Countersink Drill Set
A countersink drill set typically refers to a collection of six tools designed for countersinking operations in woodworking or metalworking. Each set usually includes six individual countersink drills with varying sizes or angles. Countersinking is a process that involves creating a conical hole in a material, allowing the head of a screw or bolt to sit flush with or below the surface. These drill sets are essential for achieving a professional finish in various applications where a smooth and even surface is desired, such as in carpentry, metal fabrication, or DIY projects.
Finishing Sander
The finishing sander is a high-performance power tool designed to deliver smooth, even surfaces on wood, metal, or painted materials. Its ergonomic design allows for comfortable handling during extended use, while its powerful motor ensures consistent sanding performance. Perfect for removing minor imperfections, preparing surfaces for paint or varnish, and achieving a professional-quality finish, this tool is ideal for carpenters, woodworkers, DIY enthusiasts, and home improvement projects. The finishing sander is compatible with a variety of sanding pads and accessories, making it versatile for different applications and finishing requirements.
Flat Knotted Wire Wheel
A Flat Knotted Wire Wheel refers to a rotating tool used in various applications, typically in metalworking and surface preparation. It consists of a wheel-shaped assembly with wire bristles that are tightly twisted or "knotted" together. The wire bristles can be made of steel or other durable materials, and they are arranged in a radial pattern around the wheel.
Knotted wire wheels are commonly attached to power tools such as angle grinders or bench grinders. They are employed for tasks like removing rust, paint, scale, or other surface contaminants from metal surfaces, as well as for deburring or blending welds. The tightly twisted configuration of the wire bristles enhances the wheel's durability and effectiveness in tackling tough materials and applications.
These wheels are available in various sizes and designs to suit different tasks, and they are known for their abrasive action, making them valuable tools in metal fabrication, construction, and maintenance work.
Forstner Drill Bits
A Forstner drill bit is a specialized cutting tool used in woodworking to create flat-bottomed holes with smooth sides. Unlike traditional twist or spade drill bits, Forstner bits are characterized by a cylindrical shape with a flat bottom and a rim that cuts the perimeter of the hole. These bits are well-suited for precision drilling tasks, such as creating boreholes for dowels or hinge cups, as they produce clean and accurate results, minimizing tear-out and splintering in the wood. Forstner drill bits are commonly used in cabinetry, furniture making, and other woodworking applications where precise and clean hole drilling is essential.
Gasoline Hedge Trimmer
A gasoline hedge trimmer is a handheld gardening tool powered by a gasoline engine, designed for trimming and shaping hedges, bushes, and shrubs. It consists of a cutting blade or blades, typically reciprocating, attached to a long shaft with a handle or grip for ease of use. The gasoline engine provides the necessary power to drive the blades, offering mobility and independence from electrical outlets, making it suitable for use in outdoor settings where access to electricity may be limited. Gasoline hedge trimmers are valued for their versatility, allowing users to manicure and maintain landscaping with efficiency and precision.


 Acrylic Sealants
Acrylic Sealants Construction Adhesives
Construction Adhesives Double-Sided Tape
Double-Sided Tape Duct Tape
Duct Tape Electrical Tape
Electrical Tape Epoxy & Resins
Epoxy & Resins Masking Tape
Masking Tape
 Automotive Wrenches & Socket Sets
Automotive Wrenches & Socket Sets Battery Chargers & Jump Starters
Battery Chargers & Jump Starters Car Jacks & Stands
Car Jacks & Stands Car Wash & Detailing Products
Car Wash & Detailing Products Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic Tools Tire Inflators
Tire Inflators Vehicle Lighting
Vehicle Lighting Oil & Lubricants
Oil & Lubricants
 Adhesives & Sealants
Adhesives & Sealants Bricks & Blocks
Bricks & Blocks Cement & Concrete
Cement & Concrete Drywall & Plaster
Drywall & Plaster Flooring (Tiles, Wood, Laminate)
Flooring (Tiles, Wood, Laminate) Lumber & Plywood
Lumber & Plywood Paints, Primers & Coatings
Paints, Primers & Coatings Insulation Materials
Insulation Materials Roofing Materials
Roofing Materials
 Circuit Breakers
Circuit Breakers Electrical Cables & Wires
Electrical Cables & Wires Switches & Sockets
Switches & Sockets Fuses & Relays
Fuses & Relays Connectors & Terminals
Connectors & Terminals Electrical Boxes & Panels
Electrical Boxes & Panels Conduit & Fittings
Conduit & Fittings Lighting Fixtures & Bulbs
Lighting Fixtures & Bulbs Extension Cords & Power Strips
Extension Cords & Power Strips
 Anchors
Anchors Bolts
Bolts Clips & Clamps
Clips & Clamps Screws
Screws Nuts
Nuts Washers
Washers Rivets
Rivets Nails
Nails Threaded Rods
Threaded Rods
 Hammers
Hammers Measuring Tools (Tapes, Levels, Calipers)
Measuring Tools (Tapes, Levels, Calipers) Screwdrivers
Screwdrivers Pliers & Cutters
Pliers & Cutters Saws & Blades
Saws & Blades Chisels & Punches
Chisels & Punches Allen Keys & Hex Keys
Allen Keys & Hex Keys Ratchets & Socket Sets
Ratchets & Socket Sets Wrenches & Spanners
Wrenches & Spanners
 Power Tool Accessories (Blades, Bits, Discs)
Power Tool Accessories (Blades, Bits, Discs) Rotary Tools
Rotary Tools Saws (Circular, Jigsaw, Reciprocating)
Saws (Circular, Jigsaw, Reciprocating) Drills & Drivers
Drills & Drivers Grinders & Sanders
Grinders & Sanders Heat Guns
Heat Guns Nail Guns
Nail Guns Impact Wrenches
Impact Wrenches Batteries & Chargers
Batteries & Chargers
 Pipes & Fittings (PVC, Copper, PEX)
Pipes & Fittings (PVC, Copper, PEX) Plumbing Tools
Plumbing Tools Pumps & Motors
Pumps & Motors Sealants & Adhesives for Plumbing
Sealants & Adhesives for Plumbing Valves & Taps
Valves & Taps Water Heaters
Water Heaters Drainage Systems
Drainage Systems Faucets & Fixtures
Faucets & Fixtures Hoses & Tubing
Hoses & Tubing
 Hinges & Latches
Hinges & Latches Hooks & Brackets
Hooks & Brackets Window Hardware
Window Hardware Chains & Cables
Chains & Cables Casters & Wheels
Casters & Wheels Shelving & Storage Systems
Shelving & Storage Systems Door Handles & Locks
Door Handles & Locks Drawer Slides & Cabinet Hardware
Drawer Slides & Cabinet Hardware
 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Respirators & Masks
Respirators & Masks Safety Glasses
Safety Glasses Safes
Safes Security Cameras
Security Cameras Gloves
Gloves Helmets
Helmets Ear Protection
Ear Protection Fire Safety Equipment
Fire Safety Equipment Locks & Padlocks
Locks & Padlocks Motion Sensors & Alarms
Motion Sensors & Alarms
 Garden Fencing
Garden Fencing Garden Furniture Hardware
Garden Furniture Hardware Lawn Mowers
Lawn Mowers Trimmers & Edgers
Trimmers & Edgers Shovels & Spades
Shovels & Spades Rakes & Hoes
Rakes & Hoes Pruning Shears & Loppers
Pruning Shears & Loppers Watering Systems (Hoses, Sprinklers, Nozzles)
Watering Systems (Hoses, Sprinklers, Nozzles)
 Interior Paints
Interior Paints Paint Brushes & Rollers
Paint Brushes & Rollers Paint Strippers & Thinners
Paint Strippers & Thinners Paint Trays & Accessories
Paint Trays & Accessories Exterior Paints
Exterior Paints Spray Paints
Spray Paints Primers & Undercoats
Primers & Undercoats Varnishes & Stains
Varnishes & Stains
 Gaskets & Seals
Gaskets & Seals Hydraulic Fittings
Hydraulic Fittings Industrial Fasteners
Industrial Fasteners Industrial Hoses
Industrial Hoses Lubricants & Greases
Lubricants & Greases Metal Sheets & Bars
Metal Sheets & Bars Bearings & Bushings
Bearings & Bushings Belts & Pulleys
Belts & Pulleys
 HVAC Filters
HVAC Filters Insulation for HVAC
Insulation for HVAC Air Conditioners
Air Conditioners Refrigerants
Refrigerants Ventilation Ducts & Fittings
Ventilation Ducts & Fittings Thermostats & Controllers
Thermostats & Controllers Fans & Blowers
Fans & Blowers
 Pegboards & Hooks
Pegboards & Hooks Shelving Units
Shelving Units Storage Bins & Containers
Storage Bins & Containers Toolboxes & Tool Chests
Toolboxes & Tool Chests Workbenches
Workbenches Drawer Organizers
Drawer Organizers Labeling Supplies
Labeling Supplies
 Welding Accessories (Clamps, Brushes)
Welding Accessories (Clamps, Brushes) Welding Electrodes & Rods
Welding Electrodes & Rods Welding Helmets & Gloves
Welding Helmets & Gloves Welding Machines
Welding Machines Soldering Irons & Stations
Soldering Irons & Stations Flux & Solder Wire
Flux & Solder Wire
 Generator Accessories
Generator Accessories Inverters
Inverters Portable Generators
Portable Generators Power Inverters
Power Inverters Transfer Switches
Transfer Switches Diesel & Gasoline Generators
Diesel & Gasoline Generators
 Transport Equipment: Carts, Dollies, and Hand Trucks
Transport Equipment: Carts, Dollies, and Hand Trucks Storage Solutions: Pallets, Racks, and Containers
Storage Solutions: Pallets, Racks, and Containers Lifting Equipment: Hoists, Cranes, and Jacks
Lifting Equipment: Hoists, Cranes, and Jacks Conveyors & Accessories: Belts & Rollers
Conveyors & Accessories: Belts & Rollers
 Office Chairs
Office Chairs











