Pedestal Grinder
$ 242.31 Original price was: $ 242.31.$ 230.20Current price is: $ 230.20.

Petrol Generator
$ 119.23 Original price was: $ 119.23.$ 113.27Current price is: $ 113.27.
Pellet Machine
$ 534.62 Original price was: $ 534.62.$ 507.89Current price is: $ 507.89.
WhatsApp Order
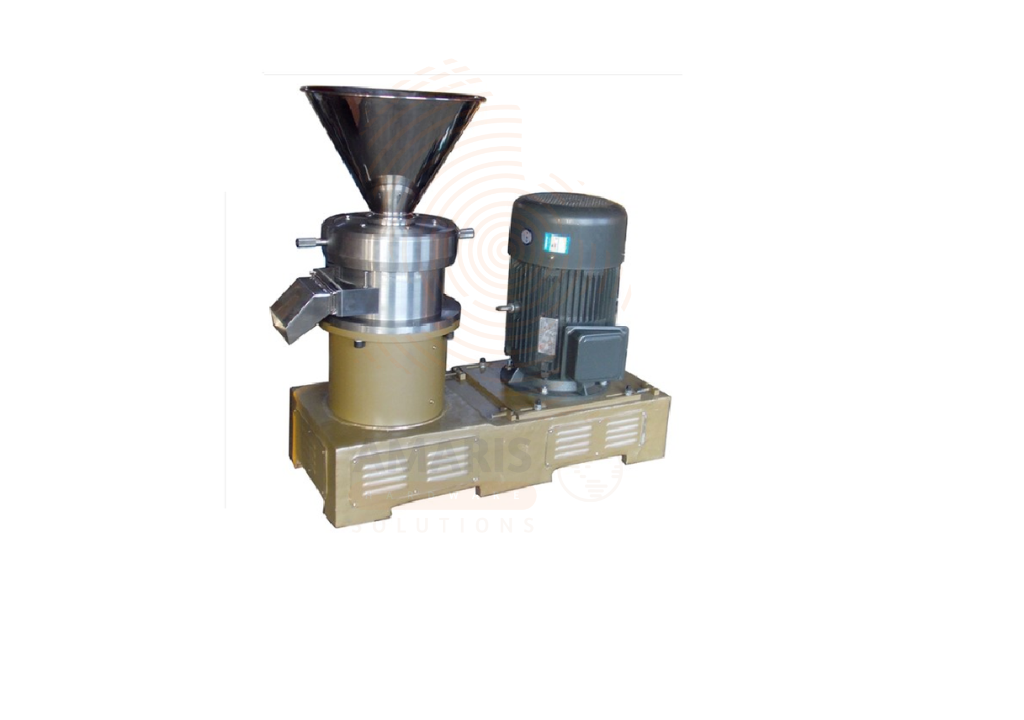
A Pellet Machine is an industrial-grade device used to compress powdered or ground raw materials into dense, cylindrical pellets. Commonly used in animal feed production, biomass energy generation, and organic fertilizer processing, it works by applying heat and mechanical pressure through a die and roller system. This transforms materials such as sawdust, straw, cornmeal, rice husks, and feed mixtures into uniform pellets. The resulting pellets are easier to handle, store, and transport, and offer improved performance in combustion, feeding, or fertilization.
Description
Table of Contents
TogglePellet Machine
Uses
-
Animal Feed Production
o Produces nutritionally balanced feed pellets for poultry, livestock, rabbits, and fish.
o Improves feed intake, digestion, and reduces feed wastage. -
Biomass Fuel Pelleting
o Converts wood chips, sawdust, rice husks, and agricultural residues into biomass pellets.
o Pellets serve as renewable, high-efficiency fuel for stoves and boilers. -
Organic Fertilizer Processing
o Compresses composted manure and organic waste into granular fertilizers.
o Enhances ease of application and nutrient distribution in soil. -
Waste Material Recycling
o Transforms unusable or dusty materials into compact, manageable pellets.
o Reduces waste volume and supports sustainable waste management. -
Fish Feed Manufacturing
o Creates floating or sinking aquatic feed with controlled nutrient content.
o Supports healthy fish growth and water cleanliness in aquaculture. -
Pre-processing for Industrial Use
o Pelletizes powdered chemicals or additives for industrial batching and mixing.
o Ensures consistency in material handling. -
Customized Farm Feed Blends
o Allows farmers to produce their own feed formulations.
o Adapts to specific nutritional needs of different livestock. -
Soil Conditioner Production
o Compresses mineral additives and conditioners into dust-free granules.
o Improves soil texture, water retention, and nutrient supply. -
Small-Scale Commercial Pelletizing
o Enables local entrepreneurs to produce marketable fuel or feed pellets.
o Encourages decentralized, cost-effective production.
SAFETY HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
Safety Precautions
-
Wear Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
o Use safety goggles, dust masks, gloves, and hearing protection.
o Avoid loose clothing near moving parts. -
Inspect Before Use
o Check rollers, die, belt, and electrical components for damage or wear.
o Ensure all guards are in place and fasteners are tightened. -
Feed Proper Material Only
o Avoid wet, sticky, or contaminated inputs that may clog or damage the machine.
o Do not insert hard objects like stones or metal. -
Avoid Overloading
o Maintain a steady, moderate feed rate to avoid motor strain and jamming.
o Use appropriate settings for material type. -
Electrical Safety
o Ensure machine is properly grounded and kept dry.
o Turn off power during maintenance or cleaning. -
Heat Awareness
o Internal components can become very hot during use—avoid contact.
o Allow machine to cool before opening for cleaning or die replacement. -
Emergency Protocols
o Familiarize yourself with emergency stop and power cut-off.
o Keep fire extinguisher nearby when processing combustible materials. -
Keep Work Area Clear
o Remove unnecessary items, tools, and debris from the workspace.
o Ensure adequate ventilation, especially when producing biomass pellets. -
Operate Only When Trained
o Only trained personnel should operate the pellet machine.
o Follow manufacturer’s manual and safety instructions at all times.
Related products
Bi-Metal Hole Saw Set
A Bi-Metal Hole Saw Set refers to a collection of nine hole saws, each constructed with a bi-metal design. A hole saw is a cylindrical cutting tool used to create holes in various materials such as wood, metal, plastic, and more. The term "bi-metal" indicates that the hole saws are made from two different types of metals, typically high-speed steel (HSS) and a more durable alloy like cobalt. This combination enhances the hole saw's cutting performance, making it suitable for a wide range of applications and providing increased durability and longevity. The set typically includes hole saws of different sizes to accommodate various hole diameters, making it a versatile tool for professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike.
Hand Rotary Barrel Pump
A hand rotary barrel pump is a manually operated pump designed to transfer liquids, typically from barrels or containers, through a rotary pumping mechanism. The pump is equipped with a hand crank or lever that, when turned, activates a rotary gear or vane system inside the pump. This rotary action creates suction, allowing the pump to draw liquid from the source container and then dispense it through a spout or nozzle. Hand rotary barrel pumps are commonly used for transferring various fluids such as oils, fuels, chemicals, and other non-corrosive liquids. They offer a portable and efficient solution for applications where a power source may be unavailable or impractical.
High Pressure Hose
A High Pressure Hose is a flexible and reinforced conduit designed to transport fluids, such as water, oil, or gas, under elevated pressure levels. Typically constructed with durable materials, such as synthetic rubber or thermoplastic compounds, high-pressure hoses are engineered to withstand and contain the force exerted by the fluid they convey. These hoses are commonly used in various industrial, automotive, and hydraulic applications where the need for efficient and secure fluid transfer at elevated pressures is paramount.
Irrigation Pump Set
An Irrigation Pump Set is a complete system designed to move water efficiently from a source—such as a river, well, pond, or tank—to agricultural fields for crop irrigation. It typically consists of a water pump (centrifugal or submersible), an engine or motor (electric or fuel-powered), piping connections, filters, and sometimes a control panel or automation features. These pump sets are vital in agricultural operations, ensuring consistent and controlled water distribution to crops. They are used across small-scale farms to large commercial operations and are compatible with various irrigation methods like drip, sprinkler, or flood systems. Irrigation pump sets are built for durability, high flow rates, and long operational hours in tough outdoor conditions.
Mini Die Polisher Kit
A MINI DIE POLISHER KIT," it could potentially be a set of 80 pieces of miniature tools and accessories designed for polishing or finishing small objects, such as jewelry, metalwork, or other intricate items.
In such a kit, you might expect to find a variety of mini die polishers, polishing compounds, abrasive tools, and other accessories that cater to detailed and precise polishing tasks. The specific contents could include items like mini polishing wheels, buffs, abrasive discs, polishing compounds, and various attachments suitable for use in a smaller-scale polishing environment.
Motor
A Motor is an electromechanical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical motion, commonly used to power machines, tools, pumps, fans, and other mechanical systems. Motors come in various types, including AC motors, DC motors, single-phase, and three-phase variants, each designed to match specific application requirements. They vary in size, torque, speed, and efficiency depending on the use case—from small appliances to industrial machinery. Electric motors are essential components in automation, manufacturing, HVAC systems, agricultural equipment, and countless mechanical operations where consistent, reliable power is required for movement or rotation. Their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and ease of integration make them a cornerstone of mechanical design.
Poker vibrator shaft
A poker vibrator shaft, also known as a concrete vibrator shaft or simply a vibrator shaft, is a tool used in construction and concrete work. It consists of a long, slender, and flexible rod or shaft, typically made of steel, with an eccentrically mounted vibrator head at one end. The vibrator head contains an electric or pneumatic motor that generates vibrations.
The primary purpose of a poker vibrator shaft is to consolidate and remove air pockets or bubbles within freshly poured concrete. When the vibrator head is immersed in the concrete mix, the vibrations it generates help to ensure uniform distribution of the concrete, enhance its density, and eliminate voids. This process, known as concrete consolidation, improves the strength and durability of the concrete structure.
Stone Crusher
A stone crusher is a heavy-duty machine designed to reduce large rocks into smaller stones, gravel, or rock dust for use in construction, road building, and other aggregate applications. These machines use mechanical force to break down stone material, typically through compression or impact. Stone crushers come in various types such as jaw crushers, cone crushers, impact crushers, and hammer crushers, each suited to specific crushing requirements. They are widely used in mining, quarrying, construction, and recycling industries to produce consistent aggregate sizes for foundations, concrete, asphalt, and more.


 Acrylic Sealants
Acrylic Sealants Construction Adhesives
Construction Adhesives Double-Sided Tape
Double-Sided Tape Duct Tape
Duct Tape Electrical Tape
Electrical Tape Epoxy & Resins
Epoxy & Resins Masking Tape
Masking Tape
 Automotive Wrenches & Socket Sets
Automotive Wrenches & Socket Sets Battery Chargers & Jump Starters
Battery Chargers & Jump Starters Car Jacks & Stands
Car Jacks & Stands Car Wash & Detailing Products
Car Wash & Detailing Products Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic Tools Tire Inflators
Tire Inflators Vehicle Lighting
Vehicle Lighting Oil & Lubricants
Oil & Lubricants
 Adhesives & Sealants
Adhesives & Sealants Bricks & Blocks
Bricks & Blocks Cement & Concrete
Cement & Concrete Drywall & Plaster
Drywall & Plaster Flooring (Tiles, Wood, Laminate)
Flooring (Tiles, Wood, Laminate) Lumber & Plywood
Lumber & Plywood Paints, Primers & Coatings
Paints, Primers & Coatings Insulation Materials
Insulation Materials Roofing Materials
Roofing Materials
 Circuit Breakers
Circuit Breakers Electrical Cables & Wires
Electrical Cables & Wires Switches & Sockets
Switches & Sockets Fuses & Relays
Fuses & Relays Connectors & Terminals
Connectors & Terminals Electrical Boxes & Panels
Electrical Boxes & Panels Conduit & Fittings
Conduit & Fittings Lighting Fixtures & Bulbs
Lighting Fixtures & Bulbs Extension Cords & Power Strips
Extension Cords & Power Strips
 Anchors
Anchors Bolts
Bolts Clips & Clamps
Clips & Clamps Screws
Screws Nuts
Nuts Washers
Washers Rivets
Rivets Nails
Nails Threaded Rods
Threaded Rods
 Hammers
Hammers Measuring Tools (Tapes, Levels, Calipers)
Measuring Tools (Tapes, Levels, Calipers) Screwdrivers
Screwdrivers Pliers & Cutters
Pliers & Cutters Saws & Blades
Saws & Blades Chisels & Punches
Chisels & Punches Allen Keys & Hex Keys
Allen Keys & Hex Keys Ratchets & Socket Sets
Ratchets & Socket Sets Wrenches & Spanners
Wrenches & Spanners
 Power Tool Accessories (Blades, Bits, Discs)
Power Tool Accessories (Blades, Bits, Discs) Rotary Tools
Rotary Tools Saws (Circular, Jigsaw, Reciprocating)
Saws (Circular, Jigsaw, Reciprocating) Drills & Drivers
Drills & Drivers Grinders & Sanders
Grinders & Sanders Heat Guns
Heat Guns Nail Guns
Nail Guns Impact Wrenches
Impact Wrenches Batteries & Chargers
Batteries & Chargers
 Pipes & Fittings (PVC, Copper, PEX)
Pipes & Fittings (PVC, Copper, PEX) Plumbing Tools
Plumbing Tools Pumps & Motors
Pumps & Motors Sealants & Adhesives for Plumbing
Sealants & Adhesives for Plumbing Valves & Taps
Valves & Taps Water Heaters
Water Heaters Drainage Systems
Drainage Systems Faucets & Fixtures
Faucets & Fixtures Hoses & Tubing
Hoses & Tubing
 Hinges & Latches
Hinges & Latches Hooks & Brackets
Hooks & Brackets Window Hardware
Window Hardware Chains & Cables
Chains & Cables Casters & Wheels
Casters & Wheels Shelving & Storage Systems
Shelving & Storage Systems Door Handles & Locks
Door Handles & Locks Drawer Slides & Cabinet Hardware
Drawer Slides & Cabinet Hardware
 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Respirators & Masks
Respirators & Masks Safety Glasses
Safety Glasses Safes
Safes Security Cameras
Security Cameras Gloves
Gloves Helmets
Helmets Ear Protection
Ear Protection Fire Safety Equipment
Fire Safety Equipment Locks & Padlocks
Locks & Padlocks Motion Sensors & Alarms
Motion Sensors & Alarms
 Garden Fencing
Garden Fencing Garden Furniture Hardware
Garden Furniture Hardware Lawn Mowers
Lawn Mowers Trimmers & Edgers
Trimmers & Edgers Shovels & Spades
Shovels & Spades Rakes & Hoes
Rakes & Hoes Pruning Shears & Loppers
Pruning Shears & Loppers Watering Systems (Hoses, Sprinklers, Nozzles)
Watering Systems (Hoses, Sprinklers, Nozzles)
 Interior Paints
Interior Paints Paint Brushes & Rollers
Paint Brushes & Rollers Paint Strippers & Thinners
Paint Strippers & Thinners Paint Trays & Accessories
Paint Trays & Accessories Exterior Paints
Exterior Paints Spray Paints
Spray Paints Primers & Undercoats
Primers & Undercoats Varnishes & Stains
Varnishes & Stains
 Gaskets & Seals
Gaskets & Seals Hydraulic Fittings
Hydraulic Fittings Industrial Fasteners
Industrial Fasteners Industrial Hoses
Industrial Hoses Lubricants & Greases
Lubricants & Greases Metal Sheets & Bars
Metal Sheets & Bars Bearings & Bushings
Bearings & Bushings Belts & Pulleys
Belts & Pulleys
 HVAC Filters
HVAC Filters Insulation for HVAC
Insulation for HVAC Air Conditioners
Air Conditioners Refrigerants
Refrigerants Ventilation Ducts & Fittings
Ventilation Ducts & Fittings Thermostats & Controllers
Thermostats & Controllers Fans & Blowers
Fans & Blowers
 Pegboards & Hooks
Pegboards & Hooks Shelving Units
Shelving Units Storage Bins & Containers
Storage Bins & Containers Toolboxes & Tool Chests
Toolboxes & Tool Chests Workbenches
Workbenches Drawer Organizers
Drawer Organizers Labeling Supplies
Labeling Supplies
 Welding Accessories (Clamps, Brushes)
Welding Accessories (Clamps, Brushes) Welding Electrodes & Rods
Welding Electrodes & Rods Welding Helmets & Gloves
Welding Helmets & Gloves Welding Machines
Welding Machines Soldering Irons & Stations
Soldering Irons & Stations Flux & Solder Wire
Flux & Solder Wire
 Generator Accessories
Generator Accessories Inverters
Inverters Portable Generators
Portable Generators Power Inverters
Power Inverters Transfer Switches
Transfer Switches Diesel & Gasoline Generators
Diesel & Gasoline Generators
 Transport Equipment: Carts, Dollies, and Hand Trucks
Transport Equipment: Carts, Dollies, and Hand Trucks Storage Solutions: Pallets, Racks, and Containers
Storage Solutions: Pallets, Racks, and Containers Lifting Equipment: Hoists, Cranes, and Jacks
Lifting Equipment: Hoists, Cranes, and Jacks Conveyors & Accessories: Belts & Rollers
Conveyors & Accessories: Belts & Rollers
 Office Chairs
Office Chairs











