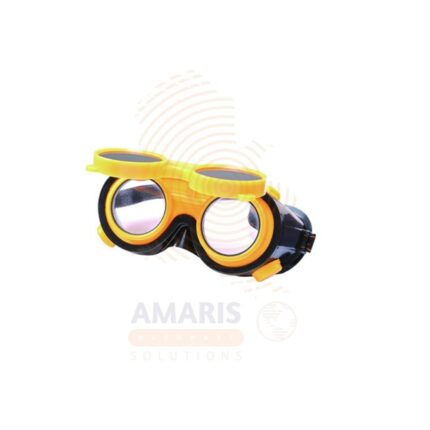

Welding Googles
$5,680.00 Original price was: $5,680.00.$5,180.00Current price is: $5,180.00.
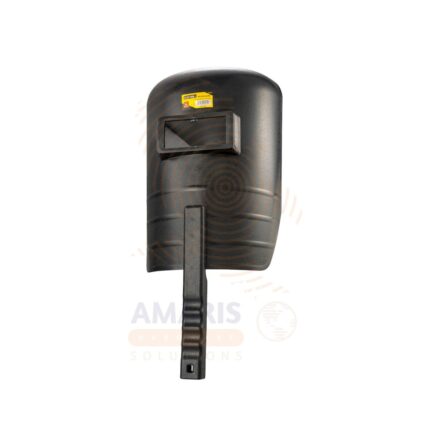

Welding Mask
$5,260.00 Original price was: $5,260.00.$4,760.00Current price is: $4,760.00.
Welding Helmet
$11,200.00 Original price was: $11,200.00.$10,700.00Current price is: $10,700.00.
WhatsApp Order
A welding helmet is a protective headgear worn by welders to shield their eyes, face, and neck from sparks, intense light, ultraviolet and infrared radiation generated during welding processes. Typically equipped with a protective lens, often auto-darkening, the helmet allows the welder to see the workpiece clearly during the non-welding phases and automatically darkens to protect the eyes when the welding arc is initiated. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and well-being of welders by preventing eye injuries and minimizing exposure to harmful radiation.
SKU:
AHS18662
Category: Welding Helmets & Gloves
Description
Welding Helmet uses
- Eye Protection: Welding helmets are designed to protect the eyes from the intense light and harmful radiation produced during welding. The helmet’s lens, especially if it is auto-darkening, darkens instantly when the welding arc is struck, shielding the eyes from potentially damaging UV and infrared rays.
- Face and Neck Protection: In addition to eye protection, welding helmets also provide coverage for the face and neck, safeguarding these areas from sparks, molten metal, and other debris produced during welding.
- Arc Visibility: Welding helmets with a transparent protective lens allow the welder to have a clear view of the workpiece and the welding area when not actively welding. This visibility is essential for accurately positioning the welding torch and monitoring the work.
- Auto-Darkening Feature: Many modern welding helmets are equipped with auto-darkening technology. This feature automatically adjusts the lens shade darkness depending on the intensity of the welding arc. It enhances comfort and convenience for the welder, as there is no need to lift the helmet between welding passes.
- Respiratory Protection: Some welding helmets are integrated with respiratory protection systems, providing an additional layer of safety by filtering out harmful fumes and particles generated during the welding process.
- Grinding and Cutting Applications: Welding helmets are often used not only for welding but also for other related processes such as grinding and cutting. The protection they offer is crucial in these activities where sparks and debris can pose hazards to the eyes and face.
- Welding in Various Environments: Welding helmets are versatile and can be used in various environments, including outdoor welding where exposure to sunlight and environmental elements can affect visibility and safety.
Reviews (0)
Be the first to review “Welding Helmet” Cancel reply
Related products
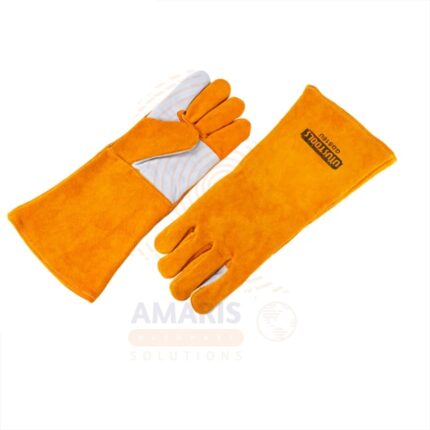
Welding Gloves
Welding gloves are specialized protective hand coverings designed to shield welders from the various hazards associated with welding processes. These gloves are typically made from heat-resistant materials such as leather or flame-resistant fabrics, providing insulation against the intense heat generated during welding. Additionally, welding gloves offer protection against sparks, molten metal, and UV radiation produced during welding operations. They play a crucial role in ensuring the safety of welders by minimizing the risk of burns, cuts, and other injuries to the hands and wrists while allowing for dexterity and control during the welding process.


 Acrylic Sealants
Acrylic Sealants Adhesive Application Tools
Adhesive Application Tools Construction Adhesives
Construction Adhesives Double-Sided Tape
Double-Sided Tape Masking Tape
Masking Tape Epoxy & Resins
Epoxy & Resins Duct Tape
Duct Tape Electrical Tape
Electrical Tape
 Auto Body Repair Tools
Auto Body Repair Tools Automotive Wrenches & Socket Sets
Automotive Wrenches & Socket Sets Battery Chargers & Jump Starters
Battery Chargers & Jump Starters Car Jacks & Stands
Car Jacks & Stands Car Wash & Detailing Products
Car Wash & Detailing Products Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic Tools Tire Inflators & Wheel Tools
Tire Inflators & Wheel Tools Oil & Lubricants
Oil & Lubricants Vehicle Lighting
Vehicle Lighting Suspension Tools
Suspension Tools Vehicle Maintenance Tools
Vehicle Maintenance Tools
 Adhesives & Sealants
Adhesives & Sealants Bricks & Blocks
Bricks & Blocks Cement & Concrete
Cement & Concrete Drywall & Plaster
Drywall & Plaster Insulation Materials
Insulation Materials Roofing Materials
Roofing Materials Paints, Primers & Coatings
Paints, Primers & Coatings Marking & Layout Tools
Marking & Layout Tools Quarry Machinery
Quarry Machinery
 Electric Motors
Electric Motors Electrical Boxes & Panels
Electrical Boxes & Panels Electrical Cables & Wires
Electrical Cables & Wires Extension Cords & Power Strips
Extension Cords & Power Strips Fuses & Relays
Fuses & Relays Lighting Fixtures & Bulbs
Lighting Fixtures & Bulbs Conduit & Fittings
Conduit & Fittings Cable Management
Cable Management Measuring & Test Equipment
Measuring & Test Equipment Circuit Breakers
Circuit Breakers Connectors & Terminals
Connectors & Terminals Switches & Sockets
Switches & Sockets
 Screws
Screws Bolts
Bolts Nuts
Nuts Washers
Washers Rivets & Riveter
Rivets & Riveter Anchors
Anchors Nails
Nails Threaded Rods
Threaded Rods Clips & Clamps
Clips & Clamps
 Garden Fencing
Garden Fencing Garden Furniture Hardware
Garden Furniture Hardware Agricultural Machinery
Agricultural Machinery Lawn Mowers
Lawn Mowers Trimmers & Edgers
Trimmers & Edgers Shovels & Spades
Shovels & Spades Rakes & Hoes
Rakes & Hoes Pruning Shears & Loppers
Pruning Shears & Loppers Watering Systems
Watering Systems Digging Equipment
Digging Equipment Pond Equipment
Pond Equipment
 Generator Accessories
Generator Accessories Inverters
Inverters Diesel & Gasoline Generators
Diesel & Gasoline Generators Power Inverters
Power Inverters Transfer Switches
Transfer Switches Portable Generators
Portable Generators Air Compressor
Air Compressor Pressure Washers
Pressure Washers Water Pumps
Water Pumps
 Fastening Tools
Fastening Tools Files & Rasps
Files & Rasps Glass working Tools
Glass working Tools Hammers
Hammers Hand Tool Accessories
Hand Tool Accessories Screwdrivers
Screwdrivers Wrenches & Spanners
Wrenches & Spanners Pliers & Cutters
Pliers & Cutters Saws & Blades
Saws & Blades Measuring Tools
Measuring Tools Chisels & Punches
Chisels & Punches Allen Keys & Hex Keys
Allen Keys & Hex Keys Ratchets & Socket Sets
Ratchets & Socket Sets Drilling & Tapping Tools
Drilling & Tapping Tools Pry Bars & Demolition Tools
Pry Bars & Demolition Tools Pulling & Extraction Tools
Pulling & Extraction Tools Punching & Perforating Tools
Punching & Perforating Tools Scrapers & Abrasive Tools
Scrapers & Abrasive Tools Utility Knives
Utility Knives Woodworking Tools
Woodworking Tools Clamps & Vises
Clamps & Vises
 Hinges & Latches
Hinges & Latches Hooks & Brackets
Hooks & Brackets Door Handles & Locks
Door Handles & Locks Drawer Slides & Cabinet Hardware
Drawer Slides & Cabinet Hardware Window Hardware
Window Hardware Chains & Cables
Chains & Cables Casters & Wheels
Casters & Wheels Shelving & Storage Systems
Shelving & Storage Systems Cutting Tools
Cutting Tools
 Fans & Blowers
Fans & Blowers HVAC Filters
HVAC Filters Insulation for HVAC
Insulation for HVAC Air Conditioners
Air Conditioners Ventilation Ducts & Fittings
Ventilation Ducts & Fittings Thermostats & Controllers
Thermostats & Controllers Refrigerants
Refrigerants
 Food Processing Machinery
Food Processing Machinery Gaskets & Seals
Gaskets & Seals Harvesting Equipment
Harvesting Equipment Hydraulic Fittings
Hydraulic Fittings Industrial Fasteners
Industrial Fasteners Industrial Hoses
Industrial Hoses Bearings & Bushings
Bearings & Bushings Belts & Pulleys
Belts & Pulleys Lubricants & Greases
Lubricants & Greases Metal Sheets & Bars
Metal Sheets & Bars Agricultural Processing Machinery
Agricultural Processing Machinery Poultry Processing Equipment
Poultry Processing Equipment
 Lifting Equipment
Lifting Equipment Transport Equipment
Transport Equipment Storage Solutions
Storage Solutions Conveyors and Accessories
Conveyors and Accessories Construction Machinery
Construction Machinery Screening Equipment
Screening Equipment Heavy Machinery
Heavy Machinery
 Paint Brushes & Rollers
Paint Brushes & Rollers Paint Sprayers & Accessories
Paint Sprayers & Accessories Paint Strippers & Thinners
Paint Strippers & Thinners Paint Trays & Accessories
Paint Trays & Accessories Primers & Undercoats
Primers & Undercoats Interior Paints
Interior Paints Exterior Paints
Exterior Paints Varnishes & Stains
Varnishes & Stains Spray Paints
Spray Paints
 Pipes & Fittings
Pipes & Fittings Plumbing Tools
Plumbing Tools Pumps & Motors
Pumps & Motors Valves & Taps
Valves & Taps Faucets & Fixtures
Faucets & Fixtures Hoses & Tubing
Hoses & Tubing Water Heaters
Water Heaters Drainage Systems
Drainage Systems Sealants & Adhesives for Plumbing
Sealants & Adhesives for Plumbing
 Nail Guns
Nail Guns Outdoor Power Equipment
Outdoor Power Equipment Planers or Woodworking Power Tools
Planers or Woodworking Power Tools Pneumatic Tool
Pneumatic Tool Power Tool Accessories
Power Tool Accessories Drills & Drivers
Drills & Drivers Saws
Saws Grinders & Sanders
Grinders & Sanders Heat Guns
Heat Guns Impact Wrenches
Impact Wrenches Batteries & Chargers
Batteries & Chargers Construction Power Tools
Construction Power Tools Cutting Tools
Cutting Tools Demolition & Breaking Tools
Demolition & Breaking Tools Router
Router Woodworking Machinery
Woodworking Machinery
 Safes
Safes Security Cameras
Security Cameras Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Fire Safety Equipment
Fire Safety Equipment Locks & Padlocks
Locks & Padlocks Motion Sensors & Alarms
Motion Sensors & Alarms
 Shelving Units
Shelving Units Storage Bins & Containers
Storage Bins & Containers Toolboxes & Tool Chests
Toolboxes & Tool Chests Pegboards & Hooks
Pegboards & Hooks Workbenches
Workbenches Drawer Organizers
Drawer Organizers Labeling Supplies
Labeling Supplies
 Flux & Solder Wire
Flux & Solder Wire Soldering Irons & Stations
Soldering Irons & Stations Welding Accessories
Welding Accessories Welding Electrodes & Rods
Welding Electrodes & Rods Welding Helmets & Gloves
Welding Helmets & Gloves Welding Machines
Welding Machines Welding Safety Equipment
Welding Safety Equipment Gas Equipment – Regulators & Gauges
Gas Equipment – Regulators & Gauges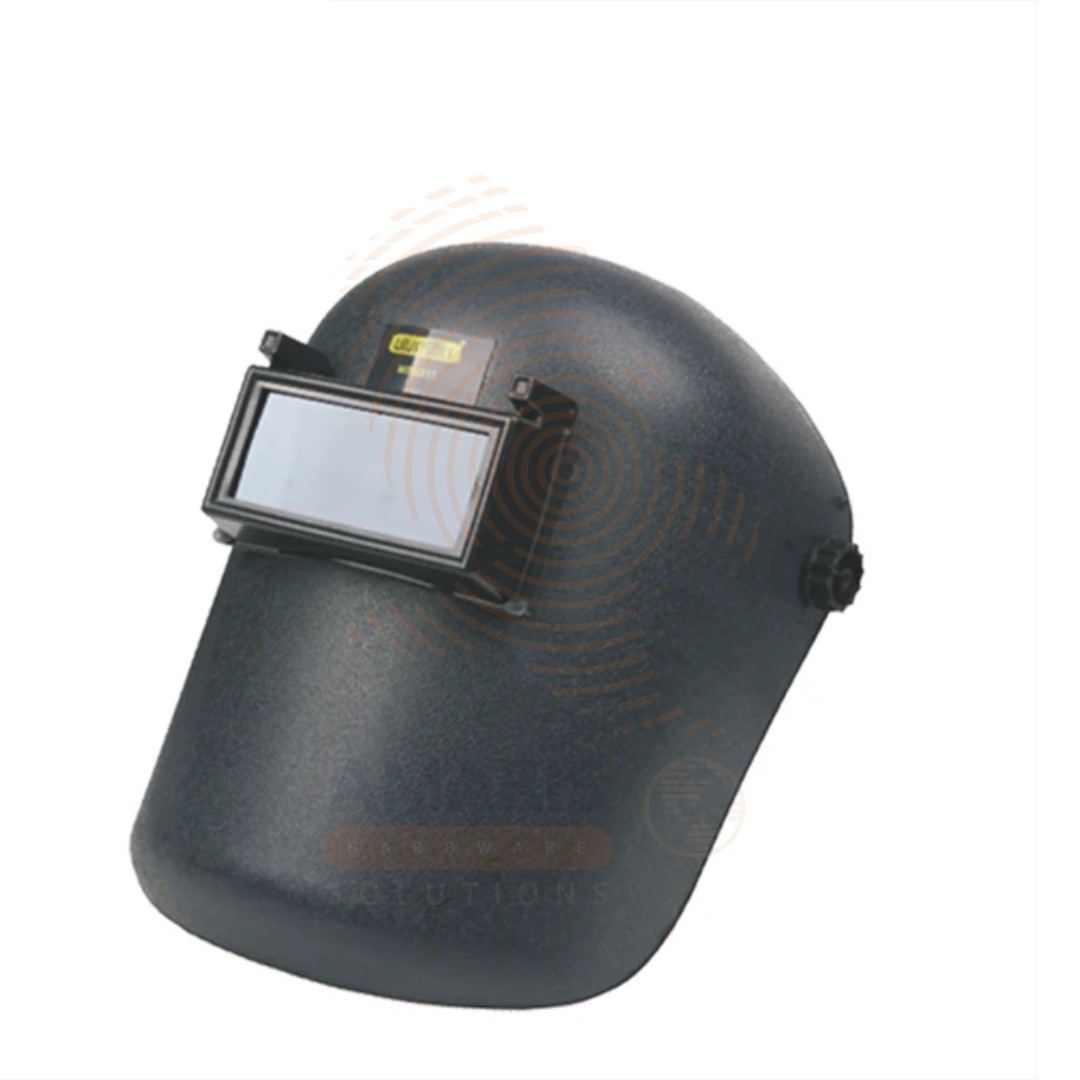






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.