Electric Brush Cutter
$ 30.77 Original price was: $ 30.77.$ 29.23Current price is: $ 29.23.

Electric Hammer Drill
$ 16.63 Original price was: $ 16.63.$ 15.80Current price is: $ 15.80.
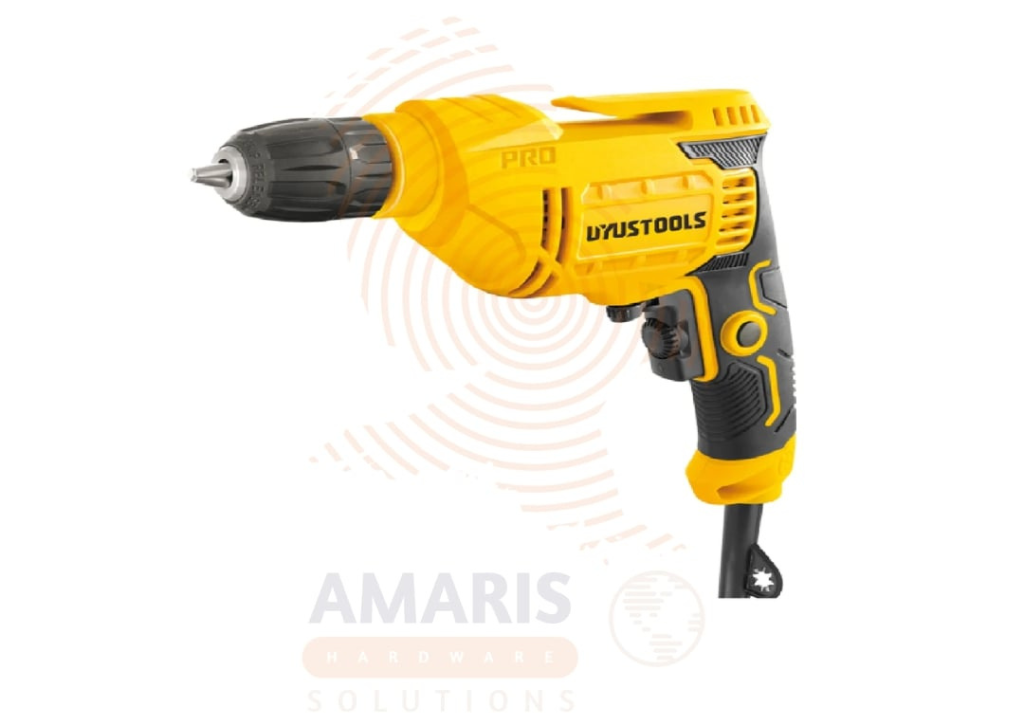
Electric Drill
$ 30.38 Original price was: $ 30.38.$ 29.77Current price is: $ 29.77.
WhatsApp Order
An electric drill is a handheld power tool that utilizes an electric motor to rotate a drill bit, enabling it to create holes in various materials such as wood, metal, plastic, and masonry. It typically consists of a trigger for controlling the speed, a grip for comfortable handling, and a chuck that securely holds and allows for the interchange of different drill bits. Electric drills are widely used in construction, woodworking, metalworking, and various DIY applications for tasks such as drilling holes, driving screws, and other fastening operations.
Categories: Drills & Drivers, POWER TOOLS
Tags: construction tool, corded drill, DIY tool, drill bits, electric drill, metalworking tool, power tool, woodworking tool, workshop tool
Description
Table of Contents
ToggleElectric Drill
Uses
-
Drilling Holes:
-
Woodworking: Electric drills are commonly used to create holes in wood for various purposes such as assembling furniture, installing hardware, or crafting.
-
Metalworking: Drills equipped with appropriate bits can bore holes in metal for tasks like installing screws or bolts.
-
-
Driving Screws:
-
Electric drills, especially those with adjustable torque settings, are employed for driving screws into different materials. This is particularly useful for tasks like assembling furniture or constructing structures.
-
-
Masonry Work:
-
With specialized masonry drill bits, electric drills can be used to drill holes in concrete, brick, or other masonry materials. This is crucial in construction and renovation projects.
-
-
Mixing and Stirring:
-
Some electric drills come with mixing attachments, allowing them to be used for stirring and mixing various substances, such as paint, adhesives, or joint compound.
-
-
Sandpaper Attachment:
-
By attaching a sanding accessory, electric drills can be transformed into power sanders for smoothing surfaces. This is particularly useful in woodworking and refinishing projects.
-
-
Polishing and Buffing:
-
Attachments for polishing and buffing can be added to electric drills, making them suitable for tasks like polishing metal surfaces or restoring the shine to certain materials.
-
-
Deburring:
-
In metalworking, electric drills are used for deburring, removing sharp edges and burrs from machined or cut metal surfaces.
-
-
Wire Brush Attachment:
-
Wire brush attachments can be used for cleaning and rust removal on metal surfaces.
-
-
Hole Saw Applications:
-
Electric drills equipped with hole saw attachments are used for cutting larger-diameter holes in materials like wood or plastic.
-
-
DIY and Home Improvement:
-
Electric drills are essential tools for a variety of do-it-yourself (DIY) and home improvement projects, from hanging shelves to installing curtain rods.
-
-
Automotive Repairs:
-
In automotive maintenance and repairs, electric drills can be used for tasks such as drilling holes, removing screws, or other applications in a workshop setting.
-
SAFETY HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
Safety Precautions
-
Wear Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
-
Eye Protection: Always wear safety glasses or goggles to protect your eyes from flying debris.
-
Gloves: Wear appropriate gloves to protect your hands from sharp edges and vibration.
-
Hearing Protection: Use earplugs or earmuffs if the drill generates high noise levels.
-
Dust Mask: Wear a mask when drilling materials that produce dust, such as wood or concrete.
-
Appropriate Clothing: Avoid loose clothing, jewelry, or long hair that could get caught in the drill.
-
-
Inspect the Drill and Accessories:
-
Examine the drill for damage, cracks, or loose parts before use.
-
Ensure cords, plugs, and battery connections are in good condition.
-
Check drill bits for wear, bending, or damage. Replace if necessary.
-
-
Choose the Right Drill Bit:
-
Select the correct type and size of bit for the material you are drilling.
-
Avoid using dull or worn-out bits to prevent slippage or overheating.
-
-
Secure the Workpiece:
-
Clamp down the material firmly to prevent movement during drilling.
-
Never hold small pieces in your hand while drilling.
-
-
Maintain Proper Posture and Grip:
-
Stand with feet shoulder-width apart for stability.
-
Hold the drill with both hands whenever possible.
-
Keep a firm, balanced stance and avoid overreaching.
-
-
Electrical Safety:
-
Ensure the drill is properly grounded if corded.
-
Keep the cord away from heat, oil, and sharp edges.
-
Do not operate a corded drill in wet or damp conditions.
-
-
Battery Safety (Cordless Drills):
-
Use only manufacturer-approved batteries and chargers.
-
Do not expose batteries to extreme heat or moisture.
-
Remove the battery before changing drill bits or performing maintenance.
-
-
Avoid Overheating and Overloading:
-
Allow the drill to rest if it becomes excessively hot.
-
Avoid forcing the drill into the material; let the drill do the work.
-
Do not use the drill for tasks beyond its rated capacity.
-
-
Control and Drill Operation:
-
Start drilling at low speed, especially when using large bits.
-
Gradually increase speed while maintaining control.
-
Keep the drill perpendicular to the work surface unless intentionally angled.
-
Be aware of kickback, especially when the bit binds in the material.
-
-
Mind Surroundings:
-
Check for hidden electrical wires, plumbing, or other obstacles before drilling.
-
Keep the workspace clear of clutter and bystanders.
-
-
Maintenance and Storage:
-
Unplug the drill or remove the battery before cleaning or maintenance.
-
Store the drill in a dry, secure location out of reach of children.
-
Regularly clean vents and moving parts to ensure proper functioning.
-
-
Training and Awareness:
-
Ensure the user is trained on proper drill operation.
-
Read and understand the manufacturer’s manual before use.
-
Do not allow inexperienced or untrained individuals to use the drill.
-
Related products
Chain Saw Adapter for Angle Grinder
Chain Saw Adapter for Angle Grinder typically refer to components that allow you to attach or use certain accessories with your chainsaw or grinder.
- Chainsaw Adapter:
- A device that enables the use of a 12-inch chainsaw blade on a chainsaw designed for a different blade size. This adapter allows you to customize or replace the original chainsaw blade with a 12-inch one, potentially for different cutting applications.
- Grinder Adapter:
- An accessory that allows you to attach a grinder to a 12-inch chainsaw, converting it into a chainsaw chain sharpener. This adapter facilitates the grinding or sharpening of the chainsaw chain, ensuring optimal cutting performance.
Circular Saw Blade for Aluminum
A circular saw blade for aluminum is a cutting tool specifically designed for use with a circular saw to cut through aluminum materials. It features specialized teeth and design elements to optimize the cutting process for aluminum, which has different characteristics compared to wood or other materials. These blades typically have a high tooth count, often with specially shaped teeth, and may incorporate coatings or materials that reduce heat buildup during cutting. The goal is to provide efficient and clean cuts through aluminum while minimizing the risk of overheating or material deformation.
Double – End Bits Set
A Double - End Bits Set typically refers to a collection of interchangeable tool bits designed for use with screwdrivers, power drills, or similar tools. Each bit in the set has two distinct ends with different types or sizes of tips, allowing the user to perform various tasks without needing multiple individual bits. These sets often include a variety of common bit types, such as Phillips, slotted, Torx, or hex, providing versatility for different screw and fastener types. The double-ended design allows users to flip the bit and switch between different tips easily, making it a convenient and space-saving solution for various applications.
Fast Charger
A fast charger is a device designed to quickly recharge compatible batteries with a voltage rating of 20 volts. The "fast" designation implies that the charger is engineered to deliver a higher charging current, allowing for a more rapid replenishment of the battery's energy capacity compared to standard chargers. This type of charger is commonly used for power tools, electronic devices, or other equipment that operates on 20V batteries, providing users with a more efficient and time-saving charging solution.
Finishing Sander
The finishing sander is a high-performance power tool designed to deliver smooth, even surfaces on wood, metal, or painted materials. Its ergonomic design allows for comfortable handling during extended use, while its powerful motor ensures consistent sanding performance. Perfect for removing minor imperfections, preparing surfaces for paint or varnish, and achieving a professional-quality finish, this tool is ideal for carpenters, woodworkers, DIY enthusiasts, and home improvement projects. The finishing sander is compatible with a variety of sanding pads and accessories, making it versatile for different applications and finishing requirements.
Flat Knotted Wire Wheel
A Flat Knotted Wire Wheel refers to a rotating tool used in various applications, typically in metalworking and surface preparation. It consists of a wheel-shaped assembly with wire bristles that are tightly twisted or "knotted" together. The wire bristles can be made of steel or other durable materials, and they are arranged in a radial pattern around the wheel.
Knotted wire wheels are commonly attached to power tools such as angle grinders or bench grinders. They are employed for tasks like removing rust, paint, scale, or other surface contaminants from metal surfaces, as well as for deburring or blending welds. The tightly twisted configuration of the wire bristles enhances the wheel's durability and effectiveness in tackling tough materials and applications.
These wheels are available in various sizes and designs to suit different tasks, and they are known for their abrasive action, making them valuable tools in metal fabrication, construction, and maintenance work.
Forstner Bits
A Forstner bit is a specialized woodworking drill bit designed for creating flat-bottomed holes with a clean and precise finish. Unlike traditional twist drill bits, Forstner bits have a cylindrical, flat-bottomed shape with a center point and cutting edges along the circumference. These bits are commonly used when a smooth and accurately sized hole without breakthrough is required in woodworking applications, such as for drilling holes for dowels or creating recesses for hardware like hinges. Forstner bits are known for their ability to produce clean and splinter-free boreholes, making them popular among woodworkers and cabinetmakers for tasks that demand precision and aesthetics.
Glass Drill Set Hexagonal Handle
A Glass Drill Set Hexagonal Handle typically refers to a collection of five drill bits specifically designed for drilling holes in glass surfaces. The term "hexagonal handle" indicates that the shank of each drill bit has a hexagonal (six-sided) shape, which can provide a better grip and prevent slipping when used with a compatible drill. These drill bits are specifically crafted for working with glass materials, offering precision and minimizing the risk of cracking or damaging the glass during the drilling process. The set may include different-sized bits to accommodate various hole diameters.


 Acrylic Sealants
Acrylic Sealants Construction Adhesives
Construction Adhesives Double-Sided Tape
Double-Sided Tape Duct Tape
Duct Tape Electrical Tape
Electrical Tape Epoxy & Resins
Epoxy & Resins Masking Tape
Masking Tape
 Automotive Wrenches & Socket Sets
Automotive Wrenches & Socket Sets Battery Chargers & Jump Starters
Battery Chargers & Jump Starters Car Jacks & Stands
Car Jacks & Stands Car Wash & Detailing Products
Car Wash & Detailing Products Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic Tools Tire Inflators
Tire Inflators Vehicle Lighting
Vehicle Lighting Oil & Lubricants
Oil & Lubricants
 Adhesives & Sealants
Adhesives & Sealants Bricks & Blocks
Bricks & Blocks Cement & Concrete
Cement & Concrete Drywall & Plaster
Drywall & Plaster Flooring (Tiles, Wood, Laminate)
Flooring (Tiles, Wood, Laminate) Lumber & Plywood
Lumber & Plywood Paints, Primers & Coatings
Paints, Primers & Coatings Insulation Materials
Insulation Materials Roofing Materials
Roofing Materials
 Circuit Breakers
Circuit Breakers Electrical Cables & Wires
Electrical Cables & Wires Switches & Sockets
Switches & Sockets Fuses & Relays
Fuses & Relays Connectors & Terminals
Connectors & Terminals Electrical Boxes & Panels
Electrical Boxes & Panels Conduit & Fittings
Conduit & Fittings Lighting Fixtures & Bulbs
Lighting Fixtures & Bulbs Extension Cords & Power Strips
Extension Cords & Power Strips
 Anchors
Anchors Bolts
Bolts Clips & Clamps
Clips & Clamps Screws
Screws Nuts
Nuts Washers
Washers Rivets
Rivets Nails
Nails Threaded Rods
Threaded Rods
 Hammers
Hammers Measuring Tools (Tapes, Levels, Calipers)
Measuring Tools (Tapes, Levels, Calipers) Screwdrivers
Screwdrivers Pliers & Cutters
Pliers & Cutters Saws & Blades
Saws & Blades Chisels & Punches
Chisels & Punches Allen Keys & Hex Keys
Allen Keys & Hex Keys Ratchets & Socket Sets
Ratchets & Socket Sets Wrenches & Spanners
Wrenches & Spanners
 Power Tool Accessories (Blades, Bits, Discs)
Power Tool Accessories (Blades, Bits, Discs) Rotary Tools
Rotary Tools Saws (Circular, Jigsaw, Reciprocating)
Saws (Circular, Jigsaw, Reciprocating) Drills & Drivers
Drills & Drivers Grinders & Sanders
Grinders & Sanders Heat Guns
Heat Guns Nail Guns
Nail Guns Impact Wrenches
Impact Wrenches Batteries & Chargers
Batteries & Chargers
 Pipes & Fittings (PVC, Copper, PEX)
Pipes & Fittings (PVC, Copper, PEX) Plumbing Tools
Plumbing Tools Pumps & Motors
Pumps & Motors Sealants & Adhesives for Plumbing
Sealants & Adhesives for Plumbing Valves & Taps
Valves & Taps Water Heaters
Water Heaters Drainage Systems
Drainage Systems Faucets & Fixtures
Faucets & Fixtures Hoses & Tubing
Hoses & Tubing
 Hinges & Latches
Hinges & Latches Hooks & Brackets
Hooks & Brackets Window Hardware
Window Hardware Chains & Cables
Chains & Cables Casters & Wheels
Casters & Wheels Shelving & Storage Systems
Shelving & Storage Systems Door Handles & Locks
Door Handles & Locks Drawer Slides & Cabinet Hardware
Drawer Slides & Cabinet Hardware
 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Respirators & Masks
Respirators & Masks Safety Glasses
Safety Glasses Safes
Safes Security Cameras
Security Cameras Gloves
Gloves Helmets
Helmets Ear Protection
Ear Protection Fire Safety Equipment
Fire Safety Equipment Locks & Padlocks
Locks & Padlocks Motion Sensors & Alarms
Motion Sensors & Alarms
 Garden Fencing
Garden Fencing Garden Furniture Hardware
Garden Furniture Hardware Lawn Mowers
Lawn Mowers Trimmers & Edgers
Trimmers & Edgers Shovels & Spades
Shovels & Spades Rakes & Hoes
Rakes & Hoes Pruning Shears & Loppers
Pruning Shears & Loppers Watering Systems (Hoses, Sprinklers, Nozzles)
Watering Systems (Hoses, Sprinklers, Nozzles)
 Interior Paints
Interior Paints Paint Brushes & Rollers
Paint Brushes & Rollers Paint Strippers & Thinners
Paint Strippers & Thinners Paint Trays & Accessories
Paint Trays & Accessories Exterior Paints
Exterior Paints Spray Paints
Spray Paints Primers & Undercoats
Primers & Undercoats Varnishes & Stains
Varnishes & Stains
 Gaskets & Seals
Gaskets & Seals Hydraulic Fittings
Hydraulic Fittings Industrial Fasteners
Industrial Fasteners Industrial Hoses
Industrial Hoses Lubricants & Greases
Lubricants & Greases Metal Sheets & Bars
Metal Sheets & Bars Bearings & Bushings
Bearings & Bushings Belts & Pulleys
Belts & Pulleys
 HVAC Filters
HVAC Filters Insulation for HVAC
Insulation for HVAC Air Conditioners
Air Conditioners Refrigerants
Refrigerants Ventilation Ducts & Fittings
Ventilation Ducts & Fittings Thermostats & Controllers
Thermostats & Controllers Fans & Blowers
Fans & Blowers
 Pegboards & Hooks
Pegboards & Hooks Shelving Units
Shelving Units Storage Bins & Containers
Storage Bins & Containers Toolboxes & Tool Chests
Toolboxes & Tool Chests Workbenches
Workbenches Drawer Organizers
Drawer Organizers Labeling Supplies
Labeling Supplies
 Welding Accessories (Clamps, Brushes)
Welding Accessories (Clamps, Brushes) Welding Electrodes & Rods
Welding Electrodes & Rods Welding Helmets & Gloves
Welding Helmets & Gloves Welding Machines
Welding Machines Soldering Irons & Stations
Soldering Irons & Stations Flux & Solder Wire
Flux & Solder Wire
 Generator Accessories
Generator Accessories Inverters
Inverters Portable Generators
Portable Generators Power Inverters
Power Inverters Transfer Switches
Transfer Switches Diesel & Gasoline Generators
Diesel & Gasoline Generators
 Transport Equipment: Carts, Dollies, and Hand Trucks
Transport Equipment: Carts, Dollies, and Hand Trucks Storage Solutions: Pallets, Racks, and Containers
Storage Solutions: Pallets, Racks, and Containers Lifting Equipment: Hoists, Cranes, and Jacks
Lifting Equipment: Hoists, Cranes, and Jacks Conveyors & Accessories: Belts & Rollers
Conveyors & Accessories: Belts & Rollers
 Office Chairs
Office Chairs











