Rice Mill
$ 338.46 Original price was: $ 338.46.$ 321.54Current price is: $ 321.54.

Roasting Cylinder
$ 134.62 Original price was: $ 134.62.$ 127.89Current price is: $ 127.89.
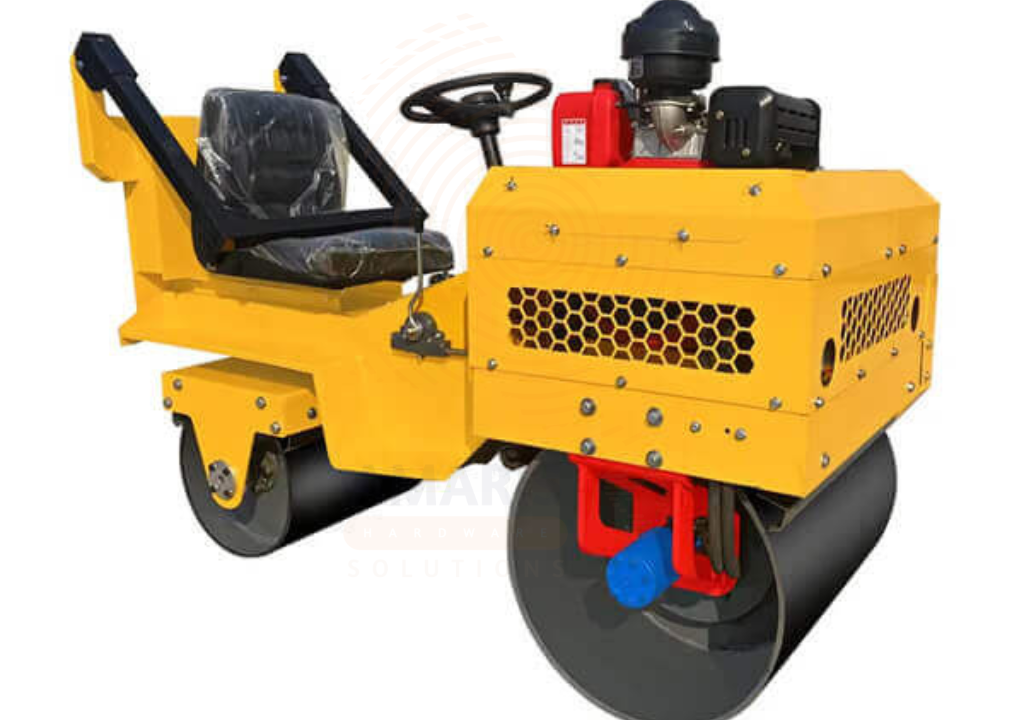
Road Roller
$ 3,088.46 Original price was: $ 3,088.46.$ 2,934.04Current price is: $ 2,934.04.
WhatsApp Order
A Road Roller is a heavy-duty compaction machine used in construction to compress soil, asphalt, gravel, and other materials to improve surface stability and load-bearing capacity. It uses large cylindrical drums—sometimes vibratory or pneumatic—to eliminate air gaps and provide a smooth, dense surface. Road rollers are essential in road building, foundations, embankments, and landfills for long-lasting structural integrity.
Description
Table of Contents
ToggleRoad Roller
Uses
-
Soil Compaction
o Used to compact soil in preparation for foundations, roads, and embankments.
o Reduces air gaps and increases the density of the ground. -
Asphalt Compaction
o Ensures smooth, long-lasting roads by compacting asphalt layers.
o Eliminates voids to prevent cracking and potholes. -
Gravel and Aggregate Compaction
o Compresses base materials under pavements and concrete surfaces.
o Enhances structural integrity of roads and platforms. -
Foundation Preparation
o Compacts ground to support structural loads without settlement.
o Used before building walls, columns, or slabs. -
Pavement Maintenance
o Recompacts surfaces after road repair or overlay work.
o Ensures evenness and longevity. -
Landfill and Waste Management
o Compresses waste in landfill operations to increase capacity. -
Embankment Construction
o Compacts fills and slopes to reduce erosion and instability. -
Runways and Airstrips
o Provides highly compacted, uniform surfaces for aviation traffic. -
Sidewalk and Pathway Construction
o Used for compacting narrower zones in pedestrian and urban projects.
SAFETY HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
Safety Precautions
-
Wear Protective Gear
o Hard hat, safety goggles, high-visibility clothing, gloves, ear protection, and steel-toed boots are required. -
Pre-Operation Inspection
o Check fluid levels, brakes, lights, drum condition, and safety mechanisms. -
Safe Operation Practices
o Only trained personnel should operate the machine.
o Avoid sudden stops, sharp turns, and steep slopes. -
Work Area Management
o Clear the area of unauthorized personnel and obstacles.
o Use signage or barriers to secure the work zone. -
Vibration Exposure Management
o Limit usage time and rotate operators if needed.
o Take regular breaks to prevent strain. -
Fuel Handling Safety
o Refuel only when engine is cool and off.
o Keep fuel away from ignition sources. -
Mounting and Dismounting Safety
o Always use steps and handholds—do not jump. -
Emergency Procedures
o Know how to activate emergency stop.
o Keep fire extinguishers and first aid nearby.
Related products
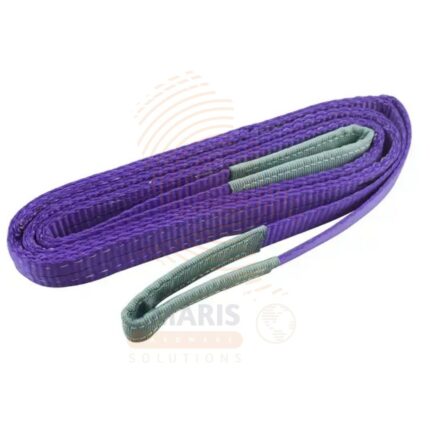
Flat Webbing Slings
A flat webbing sling is a flexible and durable lifting or towing device made from a flat strip of synthetic material, typically polyester, nylon, or polypropylene. These slings are designed for various material handling applications, such as lifting and securing loads in construction, manufacturing, and transportation industries. The flat design allows for a wide surface area, distributing the load evenly and reducing the risk of damage to the load. Flat webbing slings often feature reinforced loops at each end for attachment to lifting equipment, providing a versatile and reliable solution for lifting and moving heavy objects.
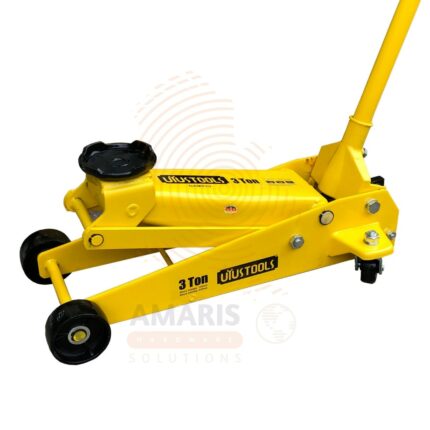
Floor Jack 3T
A Floor Jack 3T (3-ton) is a heavy-duty hydraulic lifting tool designed to raise vehicles or other heavy objects up to 3 tons (6,000 lbs) off the ground for maintenance, inspection, or repair. It uses a hydraulic cylinder and lever mechanism to provide quick and efficient lifting with minimal physical effort. The low-profile design allows it to fit under most vehicles, including cars, SUVs, and light trucks. Widely used in automotive workshops, garages, and roadside assistance, the Floor Jack 3T ensures safe and stable lifting when used with appropriate support stands.
Fork lift
A Fork lift is a powered industrial truck used to lift, carry, and transport heavy materials over short distances, commonly used in warehouses, construction sites, manufacturing facilities, and loading docks. Equipped with two forks or prongs at the front, forklifts are designed to insert under pallets or heavy items and lift them using a hydraulic system. They come in various types, including counterbalance forklifts, reach trucks, pallet jacks, and rough terrain forklifts, each tailored to specific environments and tasks. Forklifts are essential for efficient material handling, reducing manual labor, improving safety, and streamlining operations in logistics and industrial settings.
Frog Tamping Rammer
A Frog Tamping Rammer is a compact, high-impact compaction machine used in construction for compacting soil, gravel, and sand in confined or hard-to-reach areas. Unlike larger plate or roller compactors, this rammer delivers a powerful vertical force through a narrow, foot-like base (hence the name “frog”) to compact cohesive and granular soils. Commonly powered by gasoline or diesel engines, it is ideal for trench work, pipeline backfilling, foundations, road repairs, and other applications where precision and deep compaction are essential. Known for its portability and high compaction force, the frog rammer is indispensable in urban construction, civil engineering, and landscaping projects.
Hay Baler
A Hay Baler is an agricultural machine designed to compress cut and raked crops such as hay, straw, or silage into compact bales that are easy to handle, transport, and store. Hay balers come in various types, including round balers, square balers, and large rectangular balers, each producing bales of different shapes and sizes to suit specific storage and feeding needs. The baling process preserves the nutritional quality of forage and helps farmers efficiently manage fodder for livestock. Hay balers are essential equipment in modern farming, improving productivity and reducing labor.
Low Profile Floor Jack
A Low Profile Floor Jack is a type of hydraulic jack designed specifically for vehicles with low ground clearance, such as sports cars or lowered vehicles. It is characterized by its compact and sleek design, allowing it to fit easily under vehicles with minimal ground-to-frame clearance. The low-profile nature of these jacks enables users to access and lift vehicles that may be challenging or impossible to reach with standard floor jacks. These jacks typically have a lower minimum height and a shorter body compared to regular floor jacks, making them suitable for lifting vehicles with limited space between the ground and the vehicle's frame.
Vibrating Rammer
A Vibrating Rammer is a specialized construction tool designed to compact soil and other granular materials in confined or narrow spaces. It features a heavy foot plate that delivers rapid, high-impact blows combined with vibrations to achieve deep and effective compaction. This equipment is especially useful for trench work, backfill compaction around pipes, and areas inaccessible to larger compactors. The rammer’s powerful, up-and-down impact motion and vibrating action increase soil density, reduce air pockets, and improve load-bearing capacity, which is critical for stable foundations and infrastructure longevity. Commonly powered by gasoline or diesel engines, vibrating rammers are robust, portable, and essential for civil engineering, landscaping, and road construction projects.
Winch
A winch is a mechanical device used to pull in, let out, or adjust the tension of a rope, cable, or chain. It consists of a spool (or drum) operated manually or powered by electricity, hydraulics, or a combustion engine. Winches are commonly used in construction, vehicle recovery, marine applications, off-road towing, and industrial lifting. Their ability to exert controlled pulling force makes them essential in material handling and rigging operations where moving heavy objects with precision is required.


 Acrylic Sealants
Acrylic Sealants Construction Adhesives
Construction Adhesives Double-Sided Tape
Double-Sided Tape Duct Tape
Duct Tape Electrical Tape
Electrical Tape Epoxy & Resins
Epoxy & Resins Masking Tape
Masking Tape
 Automotive Wrenches & Socket Sets
Automotive Wrenches & Socket Sets Battery Chargers & Jump Starters
Battery Chargers & Jump Starters Car Jacks & Stands
Car Jacks & Stands Car Wash & Detailing Products
Car Wash & Detailing Products Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic Tools Tire Inflators
Tire Inflators Vehicle Lighting
Vehicle Lighting Oil & Lubricants
Oil & Lubricants
 Adhesives & Sealants
Adhesives & Sealants Bricks & Blocks
Bricks & Blocks Cement & Concrete
Cement & Concrete Drywall & Plaster
Drywall & Plaster Flooring (Tiles, Wood, Laminate)
Flooring (Tiles, Wood, Laminate) Lumber & Plywood
Lumber & Plywood Paints, Primers & Coatings
Paints, Primers & Coatings Insulation Materials
Insulation Materials Roofing Materials
Roofing Materials
 Circuit Breakers
Circuit Breakers Electrical Cables & Wires
Electrical Cables & Wires Switches & Sockets
Switches & Sockets Fuses & Relays
Fuses & Relays Connectors & Terminals
Connectors & Terminals Electrical Boxes & Panels
Electrical Boxes & Panels Conduit & Fittings
Conduit & Fittings Lighting Fixtures & Bulbs
Lighting Fixtures & Bulbs Extension Cords & Power Strips
Extension Cords & Power Strips
 Anchors
Anchors Bolts
Bolts Clips & Clamps
Clips & Clamps Screws
Screws Nuts
Nuts Washers
Washers Rivets
Rivets Nails
Nails Threaded Rods
Threaded Rods
 Hammers
Hammers Measuring Tools (Tapes, Levels, Calipers)
Measuring Tools (Tapes, Levels, Calipers) Screwdrivers
Screwdrivers Pliers & Cutters
Pliers & Cutters Saws & Blades
Saws & Blades Chisels & Punches
Chisels & Punches Allen Keys & Hex Keys
Allen Keys & Hex Keys Ratchets & Socket Sets
Ratchets & Socket Sets Wrenches & Spanners
Wrenches & Spanners
 Power Tool Accessories (Blades, Bits, Discs)
Power Tool Accessories (Blades, Bits, Discs) Rotary Tools
Rotary Tools Saws (Circular, Jigsaw, Reciprocating)
Saws (Circular, Jigsaw, Reciprocating) Drills & Drivers
Drills & Drivers Grinders & Sanders
Grinders & Sanders Heat Guns
Heat Guns Nail Guns
Nail Guns Impact Wrenches
Impact Wrenches Batteries & Chargers
Batteries & Chargers
 Pipes & Fittings (PVC, Copper, PEX)
Pipes & Fittings (PVC, Copper, PEX) Plumbing Tools
Plumbing Tools Pumps & Motors
Pumps & Motors Sealants & Adhesives for Plumbing
Sealants & Adhesives for Plumbing Valves & Taps
Valves & Taps Water Heaters
Water Heaters Drainage Systems
Drainage Systems Faucets & Fixtures
Faucets & Fixtures Hoses & Tubing
Hoses & Tubing
 Hinges & Latches
Hinges & Latches Hooks & Brackets
Hooks & Brackets Window Hardware
Window Hardware Chains & Cables
Chains & Cables Casters & Wheels
Casters & Wheels Shelving & Storage Systems
Shelving & Storage Systems Door Handles & Locks
Door Handles & Locks Drawer Slides & Cabinet Hardware
Drawer Slides & Cabinet Hardware
 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Respirators & Masks
Respirators & Masks Safety Glasses
Safety Glasses Safes
Safes Security Cameras
Security Cameras Gloves
Gloves Helmets
Helmets Ear Protection
Ear Protection Fire Safety Equipment
Fire Safety Equipment Locks & Padlocks
Locks & Padlocks Motion Sensors & Alarms
Motion Sensors & Alarms
 Garden Fencing
Garden Fencing Garden Furniture Hardware
Garden Furniture Hardware Lawn Mowers
Lawn Mowers Trimmers & Edgers
Trimmers & Edgers Shovels & Spades
Shovels & Spades Rakes & Hoes
Rakes & Hoes Pruning Shears & Loppers
Pruning Shears & Loppers Watering Systems (Hoses, Sprinklers, Nozzles)
Watering Systems (Hoses, Sprinklers, Nozzles)
 Interior Paints
Interior Paints Paint Brushes & Rollers
Paint Brushes & Rollers Paint Strippers & Thinners
Paint Strippers & Thinners Paint Trays & Accessories
Paint Trays & Accessories Exterior Paints
Exterior Paints Spray Paints
Spray Paints Primers & Undercoats
Primers & Undercoats Varnishes & Stains
Varnishes & Stains
 Gaskets & Seals
Gaskets & Seals Hydraulic Fittings
Hydraulic Fittings Industrial Fasteners
Industrial Fasteners Industrial Hoses
Industrial Hoses Lubricants & Greases
Lubricants & Greases Metal Sheets & Bars
Metal Sheets & Bars Bearings & Bushings
Bearings & Bushings Belts & Pulleys
Belts & Pulleys
 HVAC Filters
HVAC Filters Insulation for HVAC
Insulation for HVAC Air Conditioners
Air Conditioners Refrigerants
Refrigerants Ventilation Ducts & Fittings
Ventilation Ducts & Fittings Thermostats & Controllers
Thermostats & Controllers Fans & Blowers
Fans & Blowers
 Pegboards & Hooks
Pegboards & Hooks Shelving Units
Shelving Units Storage Bins & Containers
Storage Bins & Containers Toolboxes & Tool Chests
Toolboxes & Tool Chests Workbenches
Workbenches Drawer Organizers
Drawer Organizers Labeling Supplies
Labeling Supplies
 Welding Accessories (Clamps, Brushes)
Welding Accessories (Clamps, Brushes) Welding Electrodes & Rods
Welding Electrodes & Rods Welding Helmets & Gloves
Welding Helmets & Gloves Welding Machines
Welding Machines Soldering Irons & Stations
Soldering Irons & Stations Flux & Solder Wire
Flux & Solder Wire
 Generator Accessories
Generator Accessories Inverters
Inverters Portable Generators
Portable Generators Power Inverters
Power Inverters Transfer Switches
Transfer Switches Diesel & Gasoline Generators
Diesel & Gasoline Generators
 Transport Equipment: Carts, Dollies, and Hand Trucks
Transport Equipment: Carts, Dollies, and Hand Trucks Storage Solutions: Pallets, Racks, and Containers
Storage Solutions: Pallets, Racks, and Containers Lifting Equipment: Hoists, Cranes, and Jacks
Lifting Equipment: Hoists, Cranes, and Jacks Conveyors & Accessories: Belts & Rollers
Conveyors & Accessories: Belts & Rollers
 Office Chairs
Office Chairs











