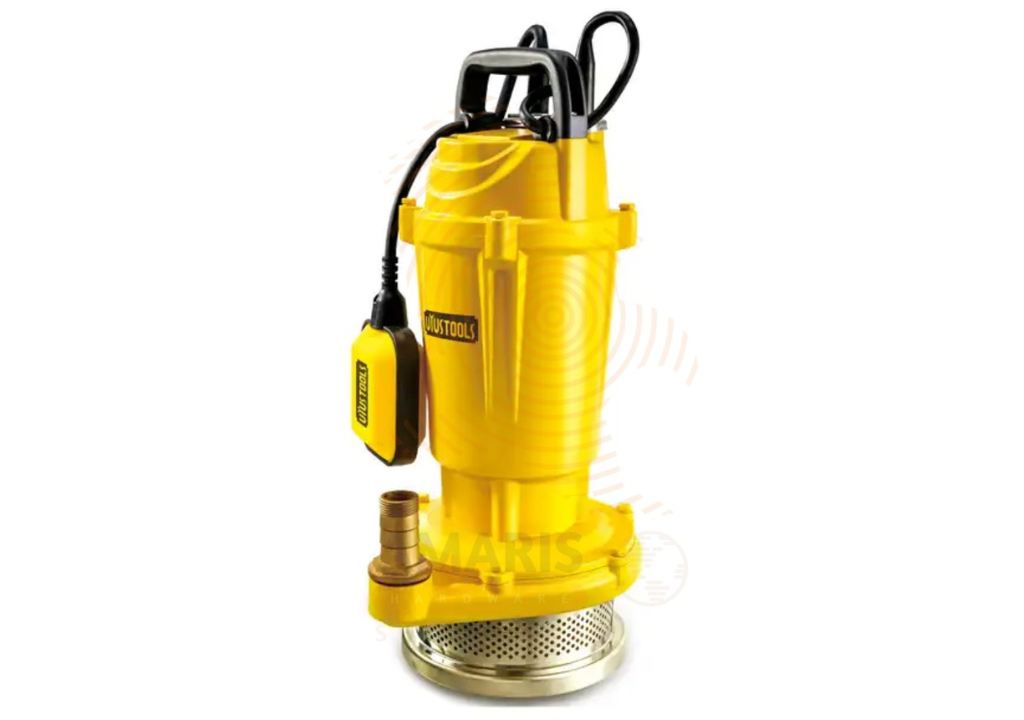

Submersible Clean Water Pump
$ 92.31 Original price was: $ 92.31.$ 87.69Current price is: $ 87.69.
A submersible clean water pump is a specialized electric pump designed to be fully submerged in water, typically for the purpose of transferring or circulating clean water. Unlike surface pumps, these devices are specifically engineered to operate underwater, effectively drawing water from the source and then discharging it to another location. Submersible clean water pumps are commonly used in various applications such as residential water supply, irrigation, drainage, and fountain systems, where the water being handled is free from debris or contaminants. These pumps are sealed to prevent water from entering the internal components, ensuring safe and efficient operation when submerged.
Table of Contents
ToggleSubmersible Clean Water Pump
Uses
-
Residential Water Supply:
-
Submersible clean water pumps are often employed in residential settings to supply clean water for drinking, cooking, bathing, and other household activities. They are commonly installed in wells, boreholes, or other water sources.
-
-
Irrigation Systems:
-
Agriculture and landscaping often rely on submersible pumps to distribute water efficiently in irrigation systems. These pumps can be submerged in wells, ponds, or other water reservoirs to provide a reliable water supply for crops or gardens.
-
-
Drainage and Dewatering:
-
Submersible pumps are used for draining and dewatering flooded areas, such as basements, construction sites, and underground parking lots. They are effective in removing excess water quickly.
-
-
Fountain and Water Feature Circulation:
-
Submersible clean water pumps are commonly used to circulate water in fountains, ponds, and other decorative water features. They help maintain water movement and aeration, contributing to the health of aquatic ecosystems.
-
-
Groundwater Management:
-
Municipalities and industrial facilities use submersible pumps for managing groundwater levels. These pumps can be installed in wells or boreholes to control water levels and prevent flooding.
-
-
Aquaculture:
-
In fish farms and aquaculture operations, submersible pumps are employed to circulate and aerate water, ensuring proper oxygenation for fish and promoting a healthy aquatic environment.
-
-
Geothermal Heating and Cooling Systems:
-
Submersible clean water pumps play a role in geothermal systems, where they help circulate water for heat exchange, either for heating buildings in winter or cooling them in summer.
-
-
Industrial Water Transfer:
-
Industries utilize submersible clean water pumps for various purposes, including transferring water between different locations within a facility or from external water sources.
-
-
Mining Operations:
-
In mining, submersible pumps are used to handle water accumulation in pits, tunnels, and other excavation sites, helping to maintain a safe working environment.
-
-
Emergency Flood Response:
-
Submersible pumps are crucial in emergency situations where rapid water removal is needed to mitigate the impact of floods or heavy rainfall.
-
Safety Precautions
-
Read the User Manual:
· Thoroughly read and understand the user manual provided by the manufacturer. It contains critical specifications for maximum submersion depth, fluid temperature limits, electrical requirements, and specific installation instructions.
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
· Wear protective gloves when handling the pump to prevent cuts and improve grip. Wear safety glasses, especially during installation and removal, and non-slip footwear when working in wet areas.
-
Inspect the Pump and Cable Before Each Use:
· Inspect the pump housing for cracks or damage. Carefully examine the power cable and plug for any cuts, abrasions, or exposed wiring. A damaged cable must be replaced before use. Ensure the inlet screen/guard is clean and intact.
-
Ensure the Pump is Fully Submerged:
· Never run the pump dry. It must be fully submerged in the fluid it is designed to pump (clean water only) during operation. Running dry will cause rapid overheating and irreparable damage to the seals and motor.
-
Use a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI):
· Always plug the pump into a GFCI-protected electrical outlet. This is a critical safety measure to prevent fatal electric shock in the event of a fault, especially in wet environments.
-
Disconnect Power for All Handling:
· Always unplug the pump from the electrical outlet before lowering it into the water, removing it, performing any maintenance, cleaning the inlet screen, or adjusting the discharge hose.
-
Maintain a Safe Power Cord Path:
· Route the power cord and discharge hose safely to prevent tripping hazards, pinching, abrasion, or damage. Keep the cord away from sharp edges, hot surfaces, and the water's path.
-
Secure the Pump and Prevent "Churn" Cycling:
· If possible, suspend the pump off the bottom using a rope or resting bracket (not by its cord) to minimize sediment intake. Use a pump float switch or ensure the water source is large enough to prevent the pump from rapidly cycling on/off as it empties and refills.
-
Prevent Freezing and Overheating:
· Do not operate the pump in freezing conditions, as ice can damage internal components. Ensure the pumped water temperature does not exceed the maximum specified by the manufacturer (typically 35-40°C / 95-104°F).
-
Use Only for Intended Clean Water:
· This pump is designed for clean water only. Do not use it to pump saltwater, chemicals, sewage, muddy water, or liquids containing solids, sand, or abrasive materials, as this will cause immediate and severe damage.
-
Prevent Back Siphonage:
· If pumping into a potable water system (e.g., a pressure tank), you must use an approved anti-siphon or backflow prevention device to prevent contamination of the water supply.
-
Store the Pump Safely:
· After use, unplug the pump, drain all water from it, and clean it according to the manual. Store it coiled in a dry, protected location away from extreme temperatures. Ensure the power cord is not kinked.


 Acrylic Sealants
Acrylic Sealants Construction Adhesives
Construction Adhesives Double-Sided Tape
Double-Sided Tape Duct Tape
Duct Tape Electrical Tape
Electrical Tape Epoxy & Resins
Epoxy & Resins Masking Tape
Masking Tape
 Automotive Wrenches & Socket Sets
Automotive Wrenches & Socket Sets Battery Chargers & Jump Starters
Battery Chargers & Jump Starters Car Jacks & Stands
Car Jacks & Stands Car Wash & Detailing Products
Car Wash & Detailing Products Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic Tools Tire Inflators
Tire Inflators Vehicle Lighting
Vehicle Lighting Oil & Lubricants
Oil & Lubricants
 Adhesives & Sealants
Adhesives & Sealants Bricks & Blocks
Bricks & Blocks Cement & Concrete
Cement & Concrete Drywall & Plaster
Drywall & Plaster Flooring (Tiles, Wood, Laminate)
Flooring (Tiles, Wood, Laminate) Lumber & Plywood
Lumber & Plywood Paints, Primers & Coatings
Paints, Primers & Coatings Insulation Materials
Insulation Materials Roofing Materials
Roofing Materials
 Circuit Breakers
Circuit Breakers Electrical Cables & Wires
Electrical Cables & Wires Switches & Sockets
Switches & Sockets Fuses & Relays
Fuses & Relays Connectors & Terminals
Connectors & Terminals Electrical Boxes & Panels
Electrical Boxes & Panels Conduit & Fittings
Conduit & Fittings Lighting Fixtures & Bulbs
Lighting Fixtures & Bulbs Extension Cords & Power Strips
Extension Cords & Power Strips
 Anchors
Anchors Bolts
Bolts Clips & Clamps
Clips & Clamps Screws
Screws Nuts
Nuts Washers
Washers Rivets
Rivets Nails
Nails Threaded Rods
Threaded Rods
 Hammers
Hammers Measuring Tools (Tapes, Levels, Calipers)
Measuring Tools (Tapes, Levels, Calipers) Screwdrivers
Screwdrivers Pliers & Cutters
Pliers & Cutters Saws & Blades
Saws & Blades Chisels & Punches
Chisels & Punches Allen Keys & Hex Keys
Allen Keys & Hex Keys Ratchets & Socket Sets
Ratchets & Socket Sets Wrenches & Spanners
Wrenches & Spanners
 Power Tool Accessories (Blades, Bits, Discs)
Power Tool Accessories (Blades, Bits, Discs) Rotary Tools
Rotary Tools Saws (Circular, Jigsaw, Reciprocating)
Saws (Circular, Jigsaw, Reciprocating) Drills & Drivers
Drills & Drivers Grinders & Sanders
Grinders & Sanders Heat Guns
Heat Guns Nail Guns
Nail Guns Impact Wrenches
Impact Wrenches Batteries & Chargers
Batteries & Chargers
 Pipes & Fittings (PVC, Copper, PEX)
Pipes & Fittings (PVC, Copper, PEX) Plumbing Tools
Plumbing Tools Pumps & Motors
Pumps & Motors Sealants & Adhesives for Plumbing
Sealants & Adhesives for Plumbing Valves & Taps
Valves & Taps Water Heaters
Water Heaters Drainage Systems
Drainage Systems Faucets & Fixtures
Faucets & Fixtures Hoses & Tubing
Hoses & Tubing
 Hinges & Latches
Hinges & Latches Hooks & Brackets
Hooks & Brackets Window Hardware
Window Hardware Chains & Cables
Chains & Cables Casters & Wheels
Casters & Wheels Shelving & Storage Systems
Shelving & Storage Systems Door Handles & Locks
Door Handles & Locks Drawer Slides & Cabinet Hardware
Drawer Slides & Cabinet Hardware
 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Respirators & Masks
Respirators & Masks Safety Glasses
Safety Glasses Safes
Safes Security Cameras
Security Cameras Gloves
Gloves Helmets
Helmets Ear Protection
Ear Protection Fire Safety Equipment
Fire Safety Equipment Locks & Padlocks
Locks & Padlocks Motion Sensors & Alarms
Motion Sensors & Alarms
 Garden Fencing
Garden Fencing Garden Furniture Hardware
Garden Furniture Hardware Lawn Mowers
Lawn Mowers Trimmers & Edgers
Trimmers & Edgers Shovels & Spades
Shovels & Spades Rakes & Hoes
Rakes & Hoes Pruning Shears & Loppers
Pruning Shears & Loppers Watering Systems (Hoses, Sprinklers, Nozzles)
Watering Systems (Hoses, Sprinklers, Nozzles)
 Interior Paints
Interior Paints Paint Brushes & Rollers
Paint Brushes & Rollers Paint Strippers & Thinners
Paint Strippers & Thinners Paint Trays & Accessories
Paint Trays & Accessories Exterior Paints
Exterior Paints Spray Paints
Spray Paints Primers & Undercoats
Primers & Undercoats Varnishes & Stains
Varnishes & Stains
 Gaskets & Seals
Gaskets & Seals Hydraulic Fittings
Hydraulic Fittings Industrial Fasteners
Industrial Fasteners Industrial Hoses
Industrial Hoses Lubricants & Greases
Lubricants & Greases Metal Sheets & Bars
Metal Sheets & Bars Bearings & Bushings
Bearings & Bushings Belts & Pulleys
Belts & Pulleys
 HVAC Filters
HVAC Filters Insulation for HVAC
Insulation for HVAC Air Conditioners
Air Conditioners Refrigerants
Refrigerants Ventilation Ducts & Fittings
Ventilation Ducts & Fittings Thermostats & Controllers
Thermostats & Controllers Fans & Blowers
Fans & Blowers
 Pegboards & Hooks
Pegboards & Hooks Shelving Units
Shelving Units Storage Bins & Containers
Storage Bins & Containers Toolboxes & Tool Chests
Toolboxes & Tool Chests Workbenches
Workbenches Drawer Organizers
Drawer Organizers Labeling Supplies
Labeling Supplies
 Welding Accessories (Clamps, Brushes)
Welding Accessories (Clamps, Brushes) Welding Electrodes & Rods
Welding Electrodes & Rods Welding Helmets & Gloves
Welding Helmets & Gloves Welding Machines
Welding Machines Soldering Irons & Stations
Soldering Irons & Stations Flux & Solder Wire
Flux & Solder Wire
 Generator Accessories
Generator Accessories Inverters
Inverters Portable Generators
Portable Generators Power Inverters
Power Inverters Transfer Switches
Transfer Switches Diesel & Gasoline Generators
Diesel & Gasoline Generators
 Transport Equipment: Carts, Dollies, and Hand Trucks
Transport Equipment: Carts, Dollies, and Hand Trucks Storage Solutions: Pallets, Racks, and Containers
Storage Solutions: Pallets, Racks, and Containers Lifting Equipment: Hoists, Cranes, and Jacks
Lifting Equipment: Hoists, Cranes, and Jacks Conveyors & Accessories: Belts & Rollers
Conveyors & Accessories: Belts & Rollers
 Office Chairs
Office Chairs











